Acute Nasal Trauma and Nose Fracture
Nasal fracture, which means nasal bone fracture, is the most common fracture of facial traumas (maxillofacial traumas). The nasal bone is the third most commonly broken bone in all body bones.
Because it is the most protruding structure of the face, the nose is a structure that is quite open to trauma. The cause of these traumas are mostly traffic accidents, assault, fall, sports and game injuries. Nasal fracture, which is more common in men and young adults, can be seen alone or with other facial bone fractures depending on the cause and severity of trauma.
It is the most common type of facial fractures and nasal fractures account for approximately 40% of all bone injuries (source: Nasal Fracture Imaging - eMedicine - Medscape)
What is the structure of the nose and what are its functions?
The nose is an important organ in the middle of the face in terms of function and aesthetics. It consists of nose, bone, cartilage and supporting structures that have functions such as smell, breathing, air heating and humidification, resistance of the airway, speech, facial expression and beauty. The outer part of the nose consists of the bone pyramid (bone roof) consisting of two nasal bones, the cartilage pyramid (cartilage roof), the movable end part of the outer nasal cartilage (lobule) and soft tissues. The inner part of the nose is divided into two nasal cavities with the nasal middle chamber (nasal septum) consisting of cartilage and bone. There are structures called nasal turbinates (conchas) in the nasal cavities.
Nasal Fracture Definition
 |
| Nasal Fracture Definition |
Nasal fracture (or a broken nose) defined as a break or crack in nasal bone. Occurs as traumatic causes such as sports injuries, accidents, falls, vehicle accidents.
In patients with nasal fractures, if broken bones glide over one another and he nose deformity is emergence this fracture type is called as "displaced nasal fracture (or depressed nasal fracture)"; if broken bone ends stand firmly in place, this nasal fracture type is called as "non-displaced nasal fracture (or non-depressed nasal fracture)". Sometimes the nasal bone fractures can occur as only crashing style.
How is the nasal fracture classification?
Depending on the form and severity of the trauma causing the nasal fracture, nasal fractures; It is classified into three types among themselves according to lateral and lateral (frontal) traumas.
Nasal Fracture Symptoms
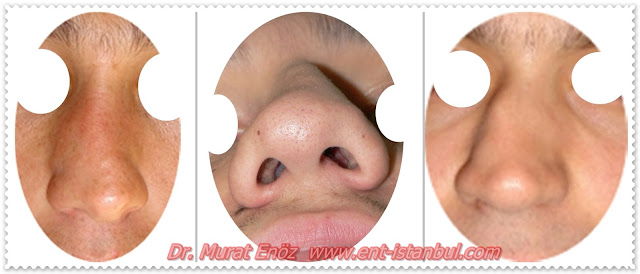 |
| Nasal Fracture Symptoms |
Symptoms of nasal fractures can be seen in:
- Nose hyperemia and bruises
- Swelling in the nose
- Nasal Deformity
- Nosebleeds
- Nasal congestion
- Hearing of crepitation sounds when touching the nose
The above, patients are seen photographs which have nasal deformities after nasal fracture.
In patients with nasal fracture depending on the severity of the trauma, nasal septum fracture, epistaxis or septal hematoma may occur.
Detailed examination of ENT can reveal these findings . X-ray of nasal bone and paranasal sinuses tomography can help for detecting the severity of the trauma.
Nasal Fracture Diagnosis
 |
| Nasal Fracture Diagnosis |
Nasal fracture diagnosis is made by history, physical examination and radiological methods. Depending on the severity of trauma in the nasal fracture, there may be pain in the nose, tenderness, swelling in the back of the nose, bruising, sliding to one side in the roof of the nose, collapse, nasal congestion and nosebleeds.
Physical examination is very important in diagnosis. Findings suggesting pain, tenderness, swelling, bruising, slips in the nasal roof, collapses, mobility, level differences between bones and cartilage, hand-protruding bone structures, and voice (crepitation) fracture during examination of fracture ends. Among these findings, crepitation is the most valuable (gold standard) finding in the diagnosis of nasal fracture. On physical examination, bleeding within the nose and slips in the middle part of the nose are findings that support nasal fracture.
The diagnosis of nasal fractures usually can be made by a simple examination and visually.
During the examination:
- Crepitation sounds on palpation of nose
- Changes in the form of nose (patient photo which taken before the trauma) be evaluated.
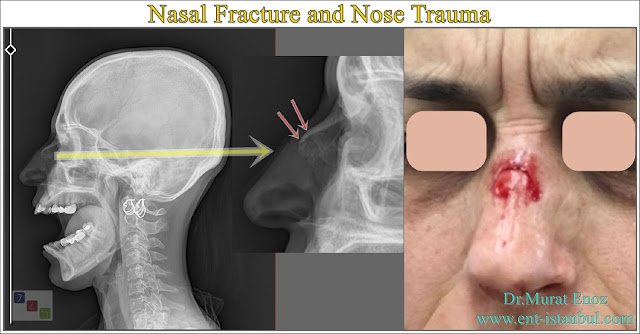
Although the benefits of radiological methods are mostly controversial, they are the methods used in terms of providing objective evidence in medicolegal aspects, in the detection of complicated fractures, fractures of other accompanying facial bones and supporting physical examination. Nasal direct side radiography (lateral os nasale radiography) is the first desired examination. Sinus x-ray (Waters x-ray), paranasal computed tomography (PNS CT), and sometimes ultrasonography in pregnant women and children are among the desired examinations. PNS CT gives the most valuable and accurate information, although it is not used as much in routine among these methods. Although PNS CT is not frequently requested due to its radiation exposure, it provides valuable information in the diagnosis especially in multiple facial bone fractures (multiple fractures) with nasal fracture.
Paranasal sinus computed tomography and the nasal bone radiography can provides more detailed information in the evaluation of the fracture line.
Nasal Bone Fracture - Overlapped Bone Line
The tomography image above belongs to the patient who had a nasal fracture after trauma 5 years ago. He was admitted to our clinic due to trauma and deformity of the nose. The patient stated that he did not receive any medical treatment when she had a nasal fracture, and that she later realized that he had a nasal fracture. When the nasal bone is fractured, the bone fracture ends may slide over each other or be displaced in another direction (displaced nasal fracture). It is important to perform nasal bone reposition with early diagnosis and early mudhaaoe. Below is the photo of the same photograph showing only the fracture line in the nasal bone (green arrow).
 |
| Photograph showing the fracture line in the nasal bone and overlapping bone lamellae (green arrow) |
Nasal Fracture Treatment
What should be done after the nose is broken?
Among the procedures to be performed after trauma, cold compress comes first. It is necessary to make a cold compress in the nose area, cheek area and the area where the upper lip is located. If you meet with the expert within a few hours after the fracture occurs, the necessary procedures will be carried out quickly. Since edema will occur after a few hours, early diagnosis is important, especially in order not to hinder the operation due to edema.
Diagnosis of the fracture, understanding whether there is a change of shape, choosing the treatment method is a very fast process. If necessary treatment is applied within a few hours, the procedure will be much easier. If you do not consult a doctor on the same day, the procedure will be delayed until the edema in the nose passes.
An x-ray or Paranasal Sinus CT and examination of the nose are required for determine to a fracture is displaced or non-displaced. However, tomography scan can be necessary to rule out other facial bone fractures.
Non-displaced fractures usually require no treatment. To follow of the patient is satisfactory and fracture heal spontaneously.
Displaced fractures require reduction to prevent permanent nasal deformity.
Nasal fracture reduction (for displaced fractures) in adults can usually be carried out in the office using local anesthesia. It can require general anesthesia in an outpatient setting especially in young children.
When and how to treat nasal fracture?
It is ideal to perform correction (fracture reduction) within the first few hours before edema develops in nasal fracture treatment. Since diffuse swelling in the nose may complicate fracture reduction, correction can be performed within 3-5 days after the swelling regresses. Treatment should not be too late since the bones will begin to boil in 7-10 days in children and 10-14 days in adults.
The form of treatment varies according to the patient's age and the type of fracture. The purpose of the treatment is to bring the broken ends to the tip, to fix them, to stabilize the unstable structures. Treatment of nasal bleeding accompanying the nasal fracture and other swelling and injuries inside and outside the nose should be treated together. Although the treatment is mostly performed with local anesthesia, general anesthesia is preferred in children, incompatible adult patients and complicated fractures.
Two methods are used in the treatment (reduction) of the fracture. Closed reduction is preferred for Type I and Type II fractures, and open reduction for Type III fractures and open fractures where adequate reduction cannot be achieved.
While the nasal bone is reduced outwards with the help of the elevator placed in the nose in closed reduction, the degree and stabilization of the fracture is adjusted from the outside with the finger. Sometimes, in type I fractures, depending on the shape of the fracture, the fracture can be reduced with the help of a finger press without the help of an elevator. After reduction, antibiotic impregnated pads are placed on both sides of the nose and splint (external splint - plaster, metal, thermoplastic material) can be applied outside the nose. Since the patient is buffered, appropriate antibiotic therapy is given. The pads are removed after two days, the splint is removed after 7-14 days.
In the open reduction, the fracture area is reached through an incision made between the cartilage from the nose and after appropriate reduction, buffer, splint and antibiotic treatment are given as in the closed reduction. In pediatric patients, more care should be taken, as damage to the growth centers in the nose can cause significant functional and aesthetic impairment in the development of the nose and face.
Nasal Fracture Reduction Technique (Closed Reduction of Nasal Fracture):
Boies or Salinger elevator inserted into the nose under the depressed fragment. Steady outward pressure can be applied on the posterior aspect of the nasal bone. Control outward pressure with counterpressure exteriorly with the other thumb. Fragments may need to be molded into the proper position.
Walsham forceps can be use also to directly grasp the nasal bone. Manipulation of the nasal bone into position can require for all efforts.
Septal reduction can be checked also. If not adequately reduced, Asch forceps can be used to elevate the nasal pyramid while applying direct pressure to the displaced portion of the septum until it is moved back into the proper position.
Septal hematoma can be checked and drained if present.
Internal packing (eg, Vaseline gauze or 8-cm Merocel) and an external splint (eg, Thermaplast, Aquaplast) can be use to stabilize reduction. Nasal dorsal skin should be protected with Steri-Strip bandage application prior to placement of the splint. While the nasal packing is in place, the patient should be on an oral antibiotic with adequate.
This reduction technique can be made with open approach. Usually, closed reduction technique can used in almost all patients.
When fracture reduction must be performed?
No matter how durable the nasal bone is, blockages may occur due to bleeding as a result of fractures. If the person has not received serious impact on the face or other parts, only if there is a non-displaced nasal fracture, early surgery is not required. But if there are fragmented fractures, surgery may be needed under general anesthesia in the early period.
The early term definition is between 24-48 hours at the latest. Because, after 24 hours after the fracture, it is a problem to put the bones separated from each other where they normally sit. When it comes to split bone fractures, it takes 3-6 months for bones to boil and wounds to heal. Here, it is necessary to fully fulfill the function of the nose, to be able to breathe easily and to be restructured aesthetically.
Post-operative Instructions for Reduction Nasal Fracture
 |
| Post-operative Instructions for Reduction Nasal Fracture |
During that period of nasal fracture healing time, activity that may cause further nasal trauma should be avoided. nasal protection used. Internal nasal packing can remove in 2-5 days and external nasal splint can remove in 7 days.
Antibiotics and pain medication are usually given for a period of first one week.
Q-tip dipped in hydrogen peroxide or warm soapy water can be used to clean the front of the nose and nostrils.
Application of cold compressors (ice pack) for 15 minutes three times a day will help reduce bruising and swelling especially first two days after the trauma.
Head elevation can help to reduce blood pressure on the facial area (sleeping with an extra pillow or two can elevate head slightly).
There are no diet restrictions, but alcohol consumption is not recommended and tobacco use is prohibitedas Nicotine decreases blood flow to the healing nasal tissues and can actually compromise wound healing.
In the first two months after broken nose glasses are inconvenient to use.
What are the problems that can develop during and after the nasal fracture?
Nasal bleeding due to the mucosal rupture in the nose with nasal fracture, especially the nasal septum hematoma which is more common in children, rupture of the brain due to the severity of the trauma and brain fluid (CSF) coming from the nose. Nasal bleeding can stop spontaneously or can be stopped with tampons. Nasal septum hematoma is an important condition especially in children, which causes complaints of nasal obstruction with the accumulation of blood in the perichondrium of the nasal septum. In treatment, blood is discharged after an incision suitable for the nasal septum. If left untreated, it causes abscesses, cartilage necrosis, and serious deformity in the nose when the child grows up. Cases of CSF coming from the nose can be mostly in severe trauma such as traffic accident, falling from height, and other head and facial bones accompanying the nasal fracture. The treatment and follow-up of this condition is multidisciplinary.
Things to consider after treatment
It is extremely important not to take any new damage after the treatment depending on the condition of the nose. After the broken area is treated, buffer is applied to the area for an average of three days. When the doctor decides to remove the tampons, the healing process is also closely monitored.
Depending on the condition of the fracture and the procedure to be applied, the removal time of plaster or plaster is approximately one week. In order for the bone structure of the nose to return to normal and not remain sensitive, it is necessary to avoid applying pressure, damage from the front or side. After the pain and tingles have passed, the healing process will end and your nose will be restored.
Broken Nose in Children
Nasal fractures can be seen in children silently and insidiously, unlike in adults. Usually a tree tree fracture in a child's nose fractures. The differences of the children's bone from the adult bone also make the fractures formed in the children featured. The fact that the child bone is more elastic and the growth cores are open is important for the follow-up and treatment of fractures in children. "Green tree fractures" are more common among these fractures. In green tree fractures, the "periosteum" membrane, which is thicker and covers the bones, remains intact. Wrist, arm, forearm, collarbone and ankle fractures are also examples of common fractures in children.
Nasal fractures are more common in adults than in children. Children's nasal bones are more difficult to break. The lower part of the nasal bone is thinner than the upper part and breaks more easily during trauma. In babies, a nasal fracture can cause nasal congestion and severe shortness of breath. Because babies do not normally breathe through their mouths (unlike adults, they depend on nasal breathing). A baby with a nasal fracture and breathing problem needs urgent treatment. Trauma causing basal nasal fracture can also cause nasal congestion by causing blood retention (septal hematoma) in the nasal septum.
Symptoms of a nasal fracture in children
Symptoms of nasal fractures in children are similar to those in adults. That is, in addition to the symptoms such as deformity, bruising, nosebleeds, nasal congestion and edema in the nose, the "crepitation sound" that may occur while sliding over the bib of the bone lamellae during the examination can be seen. Again, radiologic examinations can show broken lines in the nasal bone.
Nasal trauma in children can cause deviation of the nasal septum and nasal deformity?
Trauma during childbirth, a blow to the nose in early childhood, and most importantly, hereditary features that pass through parents cause nasal septum curvatures. Septum deviation is an extremely common condition for hereditary reasons. In particular, traumatic forces coming to the anterior region near the nasal septum may affect the buckling points in the nose, and nasal septum deviation, nasal deformity (twisted nose, crooked nose, scoliotic nose ...), and very different forms of nasal deformities may appear.
Treatment of nasal fractures in children
It is appropriate to evaluate babies and children with facial trauma with an approach to multidiscipline. After this evaluation, it is appropriate for an ear, nose and throat doctor to examine the patient for treatment. Treatment depends on the child's age, general health, and type of injury.
Things to do after nose trauma
The child will need to sit upright for some time after the injury. This helps reduce swelling of the nose. Pain medication, cold application and nasal examination are performed.
In children with displaced nasal fractures, closed nose fracture reduction is appropriate immediately. In this method, bone fragments are slid back to their places. In some cases, surgery is performed to move the bones (open reduction). It is not always possible to perform nose fracture reduction in office conditions in children. It is usually done under general anesthesia. This means that your child sleeps during the procedure and does not feel pain. In simple non-displaced nasal fractures, it is appropriate to follow up and wait in children.
The nose may need a splint and bandage after the rejection. Your child's nose may not look exactly as before. Despite all reduction procedures and precautions, especially in displaced nasal fractures, it may not be possible to obtain completely millimetric symmetry after recovery. In the following period (after the age of 18), nose surgery (rhinoplasty) may be required to make the nose look better.
Septal hematoma discharge can also be performed in some children. If the hematoma is not drained properly, damage to the septal abscess and nasal tissues may occur.
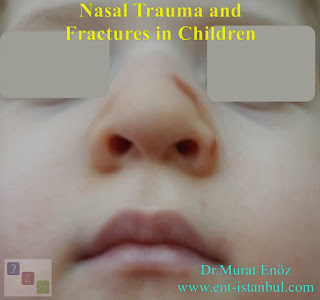
Nasal trauma and fractures in children photos
The photos below show the nose photos of a child with a "collapse" nasal fracture after nasal trauma. The patient has a collapse in the left nasal wall and an area of irritation in the skin area underneath. When viewed from the side, a small amount of "hump" can be seen after trauma. A small amount of "c-shaped light reflections" can be seen due to the displaced bone lamellae. Since there are no dilated and fragmented fractures in these fractures, simple side radiographs may not show the fracture line. In the lateral cranial radiographs below, it is seen that the periosteum region of the nasal bone is regular.
Link group where you can find detailed information about myringotomy on this website >> https://www.ent-istanbul.com/search?q=nasal+fracture
Source links:
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47







.jpg)





Comments
Post a Comment