Oral Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Infection
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is transmitted from human to human skin contact or by moist membrane primers such as vagina, anus, mouth or throat. More than 40 HPV types can be readily transmitted through direct sexual contact, from the skin and mucous membranes of infected persons, to the skin of the partners and to the mucous membranes. They can spread through vaginal, anal and oral sex. Other HPV types are responsible for sexually transmitted non-genital warts.
Some have milder effects, some of which have more than 100 virus types associated with cancer. HPV is associated with some types of cancers that are less common in both men and women. It may also cause genital warts and warts in the upper respiratory tract.
More than 50% of sexually active men and women have been infected with HPV for some time in their lives.
Most people are infected by at least one species in their lifetime. However, there are ways to prevent and reduce HPV infection. Most HPV infections do not show any symptoms and go away on their own. However, HPV is important because it can cause cervical cancer mainly in women.
There is no cure for HPV infection, but the conditions it causes can be treated.
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Infection Overview
Most people who are sexually active are in contact with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) at some point in their lifetime. HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection in the United States. More than 40 subtypes of HPV can affect the genital area and throat.HPV is spread by skin contact. Most people have contact with HPV in the genital areas during sexual intercourse. If you have sexual intercourse with the mouth, you can infect your mouth or your throat. This is commonly known as oral HPV. Likewise, there is a possibility that a person who has had frequent sexual intercourse with a person may be able to infect the other person.
Sexually transmitted HPV types are divided into two categories:
• Low-risk HPVs that do not cause cancer but can cause skin warts (also known as condylomata acuminata) in the genital area and around the anus. For example, HPV types 6 and 11 result in 90% of all genital warts. HPV types 6 and 11 also cause recurrent respiratory papillomatosis; this is a less common disease in which benign tumors grow in the airways leading from the nose and mouth to the lungs.
• High-risk HPVs that can cause cancer. Approximately a dozen high-risk HPV types have been identified. Two of these are responsible for the cancers caused by HPV type 16 and most HPV.
Most high-risk HPV infections occur without any symptoms, within 1-2 years, and do not cause cancer. However, some HPV infections may persist for many years. Permanent infections with high-risk HPV types can lead to cell changes that can cause cancer if left untreated.
What are Oral HPV Symptoms?
Oral HPV usually has no symptoms. This means that people do not realize that they are infected and are less likely to take the necessary steps to limit the spread of the disease. In some cases it is possible to form warts in the mouth or throat, but this is less common.Some types of HPV may accelerate the development of oropharyngeal cancer. If the oropharyngeal cancers, tongue, tonsils and pharyngeal walls can be found in the middle of the throat. These cells can develop from oral HPV. The early signs of oropharyngeal cancer are the following (I have included this information in the source links, but the HPV types that make warts in the mouth are different from the carcinogenic HPV types. Each HPV virus does not have high carcinogenic properties):
• difficulty swallowing
• continuous ear pain
• spitting blood
• unexplained weight loss
• swollen lymph nodes (usually painless)
• permanent sore throat
• painless swelling in the neck and cheek area
• hoarseness
If you notice any of these symptoms and know or think you have HPV infection, make an appointment with your doctor immediately.
How is Oral HPV Transmitted?
Oral HPV is the result of infection and infection when a virus enters the body, usually through a cut or small mucosal tear in the mouth. Most of the time people are caused by their sexual intercourse. More research is needed to determine exactly how oral HPV infections occur in humans.Statistics About Oral HPV
Currently, about 79 million Americans have HPV, and only 14 million people will be newly diagnosed this year.About 7 percent of Americans have oral HPV at the age of 14 to 69 years. The number of people with oral HPV has increased over the last thirty years. It is more common in males than females.
Nearly two-thirds of oropharyngeal cancers contain HPV DNA. The most common subtype of oral HPV is HPV-16. HPV-16 is considered a high-risk type. Oropharyngeal cancer is rare. About 1 percent of people have HPV-16. Every year, less than 15,000 people receive HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers.
What Are The Risk Factors For Oral HPV?
One person may have HPV infection, even though he has no symptoms and has only one sexual contact with an HPV-infected person. Any person who is sexually active (ie, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex) may take the HPV. HPV can easily pass through partners through sexual intercourse. HPV infections are more likely to occur in those who have many sex partners or who have sex with someone who has many partners.Risk factors for oral HPV include:
Oral intercourseEvidence suggests an increase in oral sexual activity, especially an increased risk of oral HPV infection if they smoke.
Multiple sexual partners
Having more than one sexual partner can increase your risk. According to Cleveland Clinic, having more than 20 sexual partners throughout your life can increase your chances of having an oral HPV infection by up to 20%.
To smoke
Smoking facilitates HPV infection. Inhaling hot fumes makes you more sensitive to tears and cuts in the mouth, and is also a risk factor in developing oral cancers.
To drink alcohol
Research has shown that high alcohol intake increases the risk of HPV infections in men. If you smoke and drink, you are at a higher risk.
Open mouth kiss
Some research has said that more open-mouthed kissing is a risk factor because it can pass into the mouth, but it is necessary to determine whether this increases the risk of oral HPV.
Gender (being a man!)
Men have a higher risk of diagnosing oral HPV than women.
Age
Oropharyngeal is a risk factor for cancer. It is more common in older adults because it takes years to develop
How is Oral HPV Diagnosed?
HPV DNA test to determine if there is HPV virus in your mouth; The negative result of the result does not prove that it is not HPV virus. Your dentist or ENT specialist can explore lesions with a cancer scan, or you may first notice lesions and make an appointment.If you have lesions, your doctor may perform a biopsy to see if the lesions are cancerous. They will also test biopsy samples for HPV. Treatment success in HPV positive cancers is generally higher.
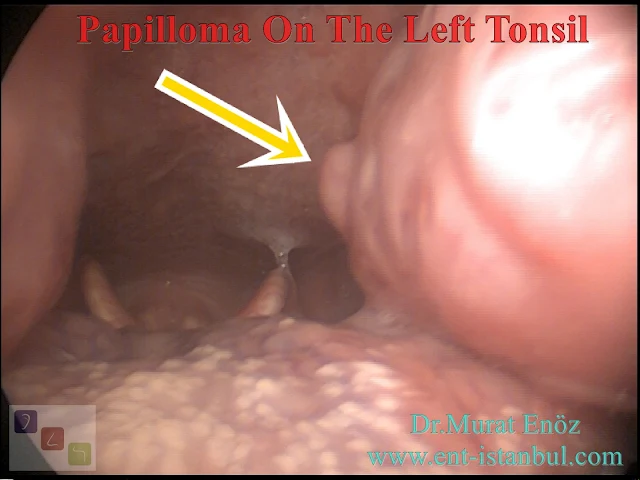
%20Infection%20(2).jpg) |
| Soft palate papilloma removal |
How is Oral HPV Treated?
Most oral HPV types are self-eliminating causing any health problems (ie, by the immune system). When HPV is caused by mouth warts; The warts may be difficult to treat with topical therapies, because the warts may also be difficult to reach. Your doctor may use any of the following methods to treat warts:• surgical removal
• cryotherapy (wart freezing)
• interferon alpha-2B injection (Intron A, Roferon-A)
HPV-induced Oropharyngeal Cancer Prognosis
If oropharyngeal cancer occurs, treatment options are available. Your treatment and prognosis depends on the stage of your cancer and whether it is associated with HPV.HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers have better results than HPV-negative cancers and have less relapse after treatment. Treatment of oropharyngeal cancer may include radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, or a combination thereof.
How to Prevent Oral HPV?
Safe sexual intercourse!
It may be useful to use condoms at all times in all sexual intercourse, but it does not prevent definitive contagion.Condoms may act as a barrier to some sexually transmitted diseases. In the case of HPV contamination, the condom does not completely eliminate the risk of the virus from spreading as HPV is exposed to skin contact with the skin. But it can reduce the risk. Condoms should never be used again.
Limit the number of sexual partners
Maybe the most important thing is to be loyal and not to have too many sexual partners ...To minimize the number of sexual partners of a person to a minimum with the HPV virus.
There must be at least eight months between sexual partners!
Studies have shown that an eight-month interval between sexual partners helps HPV infection leave the body
Perform regular HPV screening tests
If you are sexually active, it may be appropriate to have a regular test (it is written in the source links, but it is not wise to expect to be HPV positive, and DNA scanning from the oral swab may not always be a positive result ...)If you have a foreign partner, avoid having oral sex ...
Use of a condom or barrier during oral sex
The following source links have this suggestion ...Avoiding sexual activity
One way of reducing infections by the virus is that it is completely eliminated by a person who escapes all sexual intercourse. This includes oral, anal and vaginal sexual intercourse. This works best because the virus is most commonly transmitted through the genitals, mouth and throat.Ask your dentist and otolaryngologist to pay attention to the examinations!
Ask your dentist and your otorhinolaryngologist to search for your mouth for something abnormal in your six-month examinations, especially if you have had sexual intercourse. The fact that no lesions are seen in the examination does not always mean that this virus is infected with you ...Check your mouth once a month!
Once a month, make a habit of looking into your mouth for any abnormalities. If you encounter abnormal conditions, ask your doctor for an appointment.HPV vaccine
 |
| HPV vaccine / Image source: Get HPV Vaccination |
As a standard practice, if your child is older than 14 years, three shots should be performed for 6 months. In addition, three doses of 9 to 26 years old are still recommended for people with certain immunodeficiency.
Special vaccines for HPV
A vaccine is a substance that is injected into a person for protection from a particular disease. The liquid used in the vaccine will have antigens from the disease, but will not suffice to cause the disease. The body will produce antibodies to fight the disease and will develop immunity if it comes back into contact with the virusYoung children and girls who do not start or end the HPV vaccine series should be vaccinated when they were young.
The HPV vaccine is recommended for young women under 26 years of age and for men younger than 21 years. The HPV vaccine is recommended for:
• young men who have sex with men, identified as gay and bisexual, or young people who intend to have sex with men until the age of 26;
• young adults who are transgender until the age of 26; and
• Young adults with some immune system weakness (including HIV) up to the age of 26
Vaccination against HPV involves three shots for six months. You will need all three shots to be effective. The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from HPV-related illnesses.
In a recent study, oral HPV infections were said to be 88 percent lower among young adults receiving at least one dose of HPV vaccine. These vaccines help prevent oropharyngeal cancers associated with HPV.
Circumcision
Research shows that the risk of spreading HPV infection in circumcised men is reduced.Circumcision is the removal of the male foreskin from the penis. As a tight foreskin does not return easily, or for religious reasons may need to be removed for medical reasons.
Most Jewish and Islamic men are circumcised as children. This procedure also reduces the risk of infection for female partners.
Warts in the feet can be transmitted in sports halls!
If a person has plantar warts (vermic or myrmeci) standing on their toes or feet, they should refrain from spreading HPV infection by closing their bare feet by using shoes or sandals, especially in public recreation centers such as swimming baths and gyms.Do not bite your warts on hand!
If a person has a wart caused by HPV infection, they should avoid taking warts or bite their nails. Otherwise, the infection can spread to another person by tapping; it may even cause warts in its mouth!How Do I Know if HPV Is Infected?
There is no test to find a person's için HPV status Bir. In addition, there is no HPV test approved to find HPV in the mouth or throat.There are HPV tests that can be used to screen cervical cancer. These tests are recommended only for screening in women aged 30 and over. HPV tests are not recommended for screening men, adolescents or women under the age of 30 years.
Most people with HPV do not know they are infected and never develop symptoms or health problems. Some people learn that they use HPV when they take genital warts. Women can learn that they have HPV when they receive an abnormal Pap test (during cervical cancer screening). Others may learn that they have developed more serious problems than HPV, just like cancers.
In HIV-positive People, HPV Virus May Cause More Permanent Infections!
HIV (Human Immmunodeficiency Virus) - compared with negative people, people living with HIV, increased HPV persistence, higher risk of HPV-associated tumors and faster disease progression, as well as higher rates of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in various anatomical regions has a prevalence.Can HPV Vaccines Prevent HPV Infection?
The American Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved three vaccines to prevent HPV infection: Gardasil®, Gardasil® 9 and Cervarix®. These vaccines provide strong protection against new HPV infections, but are not effective in treating HPV-induced HPV infections or disease.
In Oral Infections of High-Risk HPV Viruses, Pay Attention To Your Oral Care And Do Not Use Smoking - Alcohol!
Some factors may cause a high-risk HPV-type infection to continue and possibly increase the risk of cancer. These include:• Smoking or chewing tobacco (for increased risk of oropharyngeal cancer)
• Have a weak immune system
• Poor oral hygiene (for increased risk of oropharyngeal cancer)
• Chronic inflammation
So while there is already a carcinogenic virus infection, it is necessary to pay attention to the feeding of the normal natural barrier flora. avoiding additional carcinogens ...
Search result link where you can find articles prepared by Dr. Murat Enöz about "oral HPV infection" and published on this website (you can also reach previous articles by clicking "more posts" at the end of the page) >> https://www.ent-istanbul.com/search?q=oral+HPV+infection
Source links >>
Source links >>
- HPV in the Mouth: Symptoms, Prevention, Diagnosis, and ... - Healthline
- HPV | Who Should Get Vaccine | Human Papillomavirus | CDC
- HPV Prevention - News Medical
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines - National Cancer Institute
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus) | Vaccines.gov
- STD Facts - Human papillomavirus (HPV) - CDC
- Prevention of human papillomavirus (HPV)-related tumors in people ...
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47





.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment