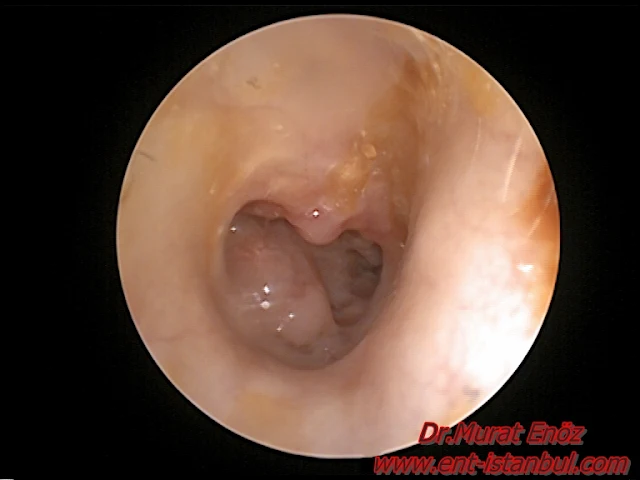
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
A perforated eardrum (or "perforations of the tympanic membrane (eardrum)") is defined as "a hole or tear in the eardrum".
There are two separate functions of the tympanic membrane:
- First, the sound waves that hit the vibration surface
- Second, is the barrier that separates the outer ear and the middle ear cavity.
Ear Anatomy
 |
| Anatomy of the ear - Image source: University of Minnesota Duluth |
Our ear consists of three separate anatomical regions: outer, middle and inner ear. There are different structures that provide sound transmission from the outer ear to the inner ear. The sound waves carried to the eardrum by the auricle and the outer ear vibrate the eardrum. The vibrating eardrum transmits vibration energy to the ossicles in the middle ear immediately adjacent. The ossial system, which acts as a lever and the vibration energy generated by the sound waves, is transmitted to our inner ear by increasing. The vibration transmitted to the inner ear stimulates the cells in different regions and provides the perception of different sounds with the nerves going from here to the brain. That is, any disease or condition that prevents or interferes with the transmission of a sound between the outer ear and the inner ear can cause hearing loss. In diseases and other conditions affecting our outer and middle ears, the sound cannot be transmitted to the inner ear. This type of hearing loss is called conductive hearing loss. In the diseases and conditions related to the inner ear, although the sound transmission; This type of hearing loss is called neural (sensorineural) hearing loss because there will be no detection of vibrations transmitted to the inner ear.
In this delicate balance of the ear, besides the task of detecting and distinguishing the sound waves, the eardrum has the task of forming a barrier between the outer ear and the middle ear.
A simple hole in the eardrum may cause recurrent middle ear infections; It may cause problems such as disruption of middle ear ossicular structures, death of inner ear nerve cells and spread of infection to brain and vessels.
The region of the middle ear is very close to the brain, facial nerve and large vessel structures. Ear anatomy and surgical experience need to be known in order to perform these operations.
In all surgical procedures for this region, as in the middle ear inflammation; There are several risks of neural injury. Especially in patients with chronic otitis media (chronic otitis media), changes in middle ear structures, bone structures may be melting. This requires the surgeon to be more careful during middle ear surgery and use a high-quality, high-resolution surgical microscope.
In the presence of cholesteatoma (inflammation foci in the middle ear that can melt the bone structures) that may sometimes coexist with chronic otitis media, there may be dissolution of the middle ear bone and ossicular structures. Sometimes, in this case, because the bone canal on the facial nerve may be fused, there is a possibility that this structure may be damaged during middle ear surgery.
Perforated Eardrum Due to Middle Ear Infection
An infection of the middle ear is one of the most common causes of a perforated eardrum. Chronic middle ear infection can cause to tympanic membran perforation and structural changes on middle ear.Perforated Eardrum Due to Trauma
A perforated eardrum is sometimes caused by a trauma to the eardrum. Traumatic causes which can cause tympanic membrane rupture are:
- Injury
- Loud noises
- Barotrauma
- Surgical trauma (such as after grommet ventilation tube insertion)
Perforated Eardrum After The Failed Ear Drum Surgery (Myringoplasty or Tympanoplasty)
Eardrum surgeries performed for tympanic membrane perforation closure. However, sometimes infection, trauma or lack of surgical technique can cause graft failure and therefore failure to heal the eardrum.
Photo above at the posterior of the ear drum, the graft is immediately adjacent to the hole.
Perforated Eardrum - Symptoms
Eardrum perforation can cause some symptoms. Hearing loss which will depend on the size of the hole in eardrum may be most common symptom. Other symptoms:
- Earache or discomfort
- A discharge of mucus from your ear
- Ringing or buzzing in your ear (tinnitus)
Perforated Eardrum - Treatment
In the video below, the eardrum surgery (myringoplasty) is animation. Dead cells are removed from the edges of the hole. Cartilage graft is placed on the hole. After placing sponges operation is terminated.
You can see detailed information about "Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment of Ear Drum Hole" at >> Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment of Ear Drum Hole / Ear Drum Repair (Tympanoplasty / Myringoplasty) in Istanbul
Tympanoplasty and myringoplasty have been described for surgical closure of the eardrum (tympanic membrane or Myrinx). In myringoplasty surgery, only the hole in the eardrum is performed; In tympanoplasty surgery, procedures are also performed for middle ear ossicles.
Types of tympanoplasty procedures
5 types of tympanoplasty procedures have been described:Type I tympanoplasty is also called “myringoplasty" ve and includes only perforated tympanic membrane restoration.
Type II tympanoplasty is used for erosion of the malleus and the eardrum. This involves placing grafts on the incus or malleus remnants.
Type III tympanoplasty is indicated in patients with intact and mobile stapes and two other ossicles (malleus-hammer bone and incus-anvil bone) that have been dissolved by inflammation. In this technique, grafts are placed on the stapes.
Type IV tympanoplasty is performed in patients with complete or partial melting of the stapes belt. It is defined as the placement of grafts on the base of mobile stapes.
Type V tympanoplasty is performed in patients with stapes base immobilized.
Endoscopic Eardrum Hole Surgery
The video above shows the transcanal endoscopic myringoplasty operation, which is performed through the ear canal without making an incision that can be seen from the outside in the external auditory canal and behind the auricle. After the operation, the patient's hearing thresholds increased.
Microscopic Transcanal Myringoplasty Video
Perforated Eardrum Repairing Surgery (Endoscopic Transcanal Myringoplasty)
Risks of Eardrum Surgery
Risks due to tympanic membrane surgery:- Damage to the middle ear ossicles and related hearing loss
- Temporary or permanent reduction in taste on one side of the tongue
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Infection
- Rarely bleeding
The Following Symptoms Are Normal After Eardrum Surgery
In eardrum surgeries, the closure of the membrane in the membrane is completed and spongosan and similar materials are placed on the membrane that stop the bleeding and fix the graft. These materials generally melt liquefied. For this reason, it is normal for the patient to have a small amount of sounds in the operative ear during eating after surgery. It is normal for these materials to mix with the blood and leave the external auditory canal, with a small amount of leakage.Ear discharge usually decreases within days.
Hearing may be impaired during this post-operative period since a tampon is placed in the external auditory canal and usually remains between 1-3 weeks.
During tympanic surgery, the chorda tympani nerve (often temporarily) may be damaged, which allows the detection of the unilateral taste sense of the 2/3 anterior part of the tongue. Reduction in taste may occur on one side of the tongue after surgery.
When the eardrum surgery is performed by incision (incision) behind the auricle, post-operative dressing from the forehead to the ear can be made and this dressing usually remains for 1 day.
If an incision was made behind the auricle; numbness in this area is normal. This numbness will decrease in a few months.
During tympanoplasty operations, ossicular surgery or mastoidectomy can be performed along with the tympanic membrane. In this case, dizziness may occur in the first few days after surgery.
After hearing the tympanic membrane, it is necessary to wait at least 6 months before the hearing can be interpreted. The reason for this is that the swollen mucosa in the middle ear should return to normal, the blood will be sucked, and the inserted membrane should pass for at least 6 months to fully merge with the normal membrane.
Postoperative Patient Care For Eardrum Surgery
- In the first week after the operation, the head is raised and sleep decreases blood pressure and edema behind the ear and middle ear cavity. After the first week, the head can be brought back to normal.- All exercise movements and daily activities that may cause air to be pushed into the middle ear cavity should be avoided.
- The mouth should not be closed during sneezing.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects for at least 2 weeks.
- To prevent constipation in the early postoperative period, it is more appropriate to feed on soft, warm and fibrous foods.
- Excessive cough can also be harmful, so medications can be used in this case
- The operated ear should be protected from water contact for the first 2 months. For this, cotton pads prepared by impregnation of petroleum jelly or ready ear plugs can be used after the ear pads are taken by the doctor. Low temperature hair dryer can be kept in the ear after surgery.
- Swimming, diving and water skiing are inconvenient for two months after surgery (I usually advise my patients to avoid swimming and water sports for at least 6 months).
- Tampers in the outer ear canal will be replaced by your doctor. These pads should not be removed without consulting your doctor.
- Strenuous athletic activities in the gym for one month after surgery should be avoided.
Eardrum Rapiring Failure
After tympanoplasty or myringoplasty, it may not be possible to close the eardrum perforations almost completely. The reasons for this can be listed as follows:
- If the hole in the eardrum is too large, insufficient contact of the membrane edges with the placed graft (usually a small perforated area may remain at the anterior border, as in the photo above). Appropriate surgical technique and providing adequate visual angle can reduce this possibility. Especially in patients with curved anterior wall of the external auditory canal and the anterior part of the tympanic membrane cannot be seen clearly with the microscope, increasing the angle of view by turning this part of the external auditory canal with the help of a drill or using an endoscopic system at the same time may facilitate a clearer visualization of this area and surgical intervention.
- Problems with surgical technique or graft placement (excision of the dead epithelial area in the eardrum and contact of the graft with this area, that is, all edges of the perforation, is very important. The placement of the graft and deepitelization of the perforation edges, the choice of surgical technique are very important)
- Various factors related to the patient such as having a flu upper respiratory tract infection, sneezing, pressure increase, water leakage in the ear immediately after the eardrum surgery
- In case of chronic infection areas such as cholesteatoma in the middle ear or mastoid cells, performing tympanic membrane operation alone may cause increased infection and perforation of the membrane. Appropriate patient selection is very important. In dry and uninfected ears, only eardrum surgery can be planned; In patients with cholesteatoma and chronic suppurative otitis media, additional operations such as mastoidectomy may be required to clear the chronic infection.
The Price of Closure Surgery for Perforation of the Eardrum in Istanbul
The cost of closure of the eardrum holes varies between 3000 - 3500 US Dollars, depending on the hospitals and the operation time in Istanbul. The average price in luxury hospitals can go up to 4500 USD. Especially in large eardrum holes, patients with ossicular chain damage, eardrum operations can be performed by removing the eardrum or processing the ossicular chain, in addition to mastoidectomy operation can be performed in patients with chronic middle ear infections, in such cases the total operation fee may increase. Again, in suitable patients, this operation can be performed without making a visible incision in the external ear canal or outside the ear, using the endoscopic technique.
Frequently Asked Questions About Eardrum Surgeries
Can you hear without an eardrum?
The eardrum has the function of a membrane, which is responsible for the transmission and collection of sound energy, which vibrates by striking sound waves, which ensures the transmission of this vibration energy to the ossicular system in the middle ear. When this membrane is punctured for various reasons, "conductive hearing loss" occurs because the energy transmission of sound waves will decrease in the first place. In the following period, since the other task of the eardrum, the "barrier surface area between the middle ear and the outer ear", was also affected, the inner ear was also affected due to recurrent middle ear infections, adding "sensorineral type hearing loss" to the table, and "mixed hearing loss". may occur. In other words, as the hole in the eardrum grows, hearing loss may increase. Even if the eardrum is completely removed, bone conduction can continue and "incomplete hearing" occurs. So "deafness" does not occur in the first place. With recurrent middle ear infections, hearing loss may deepen.
Is eardrum damage permanent?
In tympanic membrane perforations, recovery after acute traumatic ruptures is close to 100% (no water contact with the external ear canal, no repetitive trauma or infection). Spontaneous healing rate is much lower in tympanic tympanic membranes that cause fever and burns. In traumatic eardrum ruptures, only protection of the ear from water contact and follow-up are sufficient. In addition, with recurrent infections, the hole in the membrane may become permanent and eardrum surgery may be required.
How many hours does ear surgery take? (How long does it take for a perforated eardrum to close?)
While simple and short operations that require approximately 30-45 minutes of operation time are planned for small eardrum holes, the operation time may take 2-3 hours in large perforations and in operations where additional interventions to the middle ear ossicles (ossiculoplasty) and mastoidectomy are performed.
What causes a hole in eardrum?
Perforations of the eardrum can occur due to explosion, mechanical trauma, pressure trauma, infection. Sometimes it can occur even in severe acoustic trauma at close range.
How long does it take to recover from eardrum hole repair surgery? (How long is recovery for eardrum surgery?)
Although recovery is usually completed within weeks after surgery; After the closure of the large eardrum holes, the full recovery period may take up to 6 months. Recovery time may be much shorter after endoscopic transcanal tympanic membrane surgeries compared to classical tympanoplasty operations.
How successful is eardrum repair?
With the appropriate and correct technique, the correct patient selection and the patient's attention to post-operative care recommendations, the success rate can be determined to be very high. In addition, with very simple mistakes made by patients, eardrum surgery may fail, some factors that can reduce the success of eardrum surgeries:
- smoking
- sneezing with mouth closed, nose blowing,
- early ear incontinence, swimming and diving
- mechanical trauma to the ear
- Infection in the surgical field in the early period after upper respiratory tract infection
Apart from these, when there are hidden and closed infection areas such as cholesteatoma in the middle ear and mastoid bone, repairing the hole in the eardrum alone may cause the cholesteatoma to be activated and the membrane to perforate due to infections.
What are the side effects of perforated eardrum surgery? (Risks of surgery for a perforated eardrum)
After eardrum surgery, the probability of complications is very low. It is almost non-existent, especially after simple myringoplasty operations. However, in larger tympanic surgeries and additional incisions, the possibility of complications related to local wound complications and damage to surrounding tissues may increase. The technical conditions of the hospital where the operation is performed and the practice of an experienced ear surgeon are beneficial in reducing the risks.
Can facial paralysis be seen after eardrum surgery?
Temporary facial paralysis due to local anesthetics injected during eardrum surgeries can be seen; There may be a risk of permanent facial nerve damage after larger and more complicated ear surgeries such as mastoidectomy.
How can I close my ear hole without surgery?
Patients with nascent perforation of the tympanic membrane can increase the likelihood of spontaneous healing of the tympanic membrane by heeding the following recommendations:
- protect the ear from water contact
- avoiding pressure trauma to the ear (sneezing with your mouth open, not blowing your nose, avoiding air travel...)
- to pay attention to early treatment and recommendations in upper respiratory tract infections, to use decongestants to keep the nose open
- paying attention to diet and lifestyle to reduce body resistance to reduce the number of upper respiratory tract infections
In addition, the holes in the eardrum, which have existed since ancient times, can only be closed with surgical intervention. So although there is not much you can do; It is useful to protect the ear from water contact, to prevent the hole from growing and to prevent recurrent middle ear infections.
Is it possible to travel by plane with a hole in the eardrum?
In patients with a hole in the eardrum for a long time, the patient's middle ear is not affected by pressure changes, and patients do not feel anything in their ears while the plane is taking off and descending (the hole in the eardrum works like a ventilation tube). People with a healthy eardrum may feel pain when the eardrum collapses inward, especially as the plane descends. Ideal for patients who have recently had tympanic membrane bleeding (due to stretching) due to traumatic perforation of the eardrum or barotrauma to avoid air travel and diving.
How do you close a hole in your eardrum? (How do you fix a ruptured eardrum? - How do you heal an eardrum hole naturally? - How can I fix my ear hole without surgery?)
In acute tympanic membrane perforations, the possibility of spontaneous closure of the hole is high with avoidance of water contact with the ear and medical treatment. For example, in children, after acute middle ear inflammation, in cases where the eardrum is punctured and the inflammation is discharged, the hole closes close to 100% with not getting water in the ear and medical treatment. If the hole is already present, it is ideal to see an otolaryngologist and ask about the surgical procedure that needs to be done.
Is eardrum hole surgery painful? (How painful is ear drum surgery?)
In transcanal (performed through the ear canal), endoscopic or microscopic eardrum repairs, the pain and recovery time is much less than in eardrum operations in which classical skin incisions are made. Many patients want an operation with the shortest recovery and the smallest possible incision. Although incisions such as retroauricular incision made behind the auricle and Endaural incision made on the auricle, the surgeon's surgical vision increases; The amount of post-operative pain is high. The technique can be determined according to the size and location of the hole in the eardrum and the condition of the middle ear.
Can a perforated eardrum repair itself?
In newly emerged eardrum perforations, only protection of the ear from water contact and recovery with follow-up is sufficient; it is necessary to plan myringoplasty or tympanoplasty operations in the holes that have existed for a long time.
Is tympanoplasty a major surgery? (How serious is ear drum surgery?)
Eardrum surgeries are generally simple and consist of microsurgical procedures. However, when mastoidectomy, which includes cleaning the middle ear and surrounding inflamed areas, is also performed, the operation turns into a more complicated procedure. Closing only the membrane hole is a simple surgical procedure, you do not need to be afraid.
Link group where you can read articles about eardrum published on this website >> https://www.ent-istanbul.com/search?q=eardrum (You can browse other articles by clicking the more posts link at the end of the page.)
Source links:
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47









Comments
Post a Comment