Endoscopic Eardrum Surgery in Istanbul
In patients with a hole in the eardrum, the hole in the eardrum can be repaired using endoscopic and microscopic techniques through the ear canal.
Why does perforation occur in the eardrum?
Permanent perforations of the eardrum may occur for the following reasons:- A serious middle ear infection
- Recurrent middle ear infections
- Inserting foreign bodies into the ear canal
- Ear tube placement (surgical trauma)
- Pressure or sound trauma
Small eardrum holes caused by traumatic causes usually resolve spontaneously within 2 months without treatment.
In small eardrum holes, only myringoplasty to close the hole is sufficient; membrane surgery (tympanoplasty) in which ossiculoplasty is performed for problems with middle ear ossicles in large eardrum holes may be required.
- Restoring the eardrum barrier function. In this way, the risk of middle ear infection is eliminated if water escapes into the external ear canal.
- Improve hearing. By resurfacing the vibrating surface area of the eardrum, the vibration energy generated by the sound waves is transmitted more easily.
- Preventing the emergence of diseases and conditions such as facial palsy, brain abscess, meningitis due to prospective recurrent middle ear infections
During the operation, especially the new membrane, the prepared graft should be contacted to all edges of the hole. In particular, the edges of the front of the hole, if the graft does not come into contact with the opening of these areas and may cause surgery to fail.
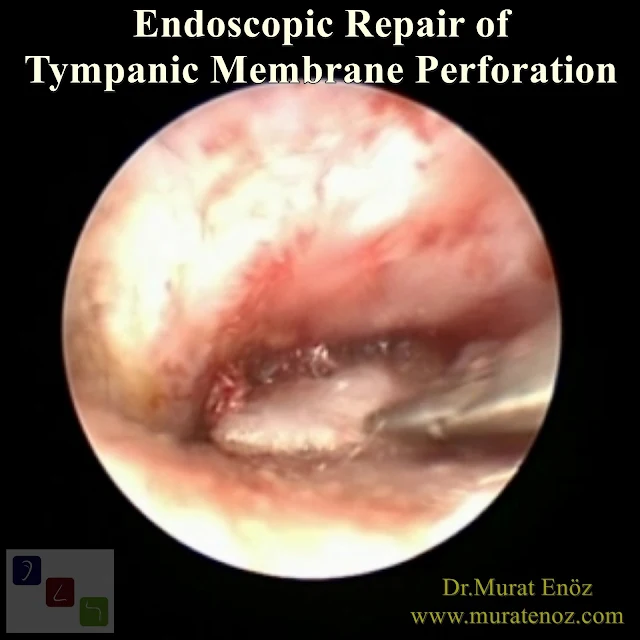
Endoscopically assisted eardrum surgery (Endoscopic Myringoplasty - Endoscope Assisted Myringoplasty, Endoscopic Myringoplasty - Endoscopic-Assisted Myringoplasty - Endoscopic Eardrum Hole Surgery - Endoscopic Repair of Tympanic Membrane Perforation) is shown to the patient with central hole (tympanic membrane central perforation) in the eardrum.
After preparing the 1 cm cartilage graft which taken from "Tragus" just in front of the ear canal,
• aspiration of the antiseptic solution poured into the external auditory canal and local anesthetic injection
• cleaning the dead cells on the edge of the hole in the eardrum
• cleansing of the middle ear adhesions
• that blood is coming from all sides of the dice and that the receipt of dead cells is controlled
• placement of cartilage parts in the middle ear
• a cartilage graft is laid over your hole (on the eardrum membrane)
• checking that the pre-peeled dried cartilage membrane is outermost and that all hole edges are closed
• It appears that the graft that has been placed has been soaked with antibiotics and spontaneously dissolvable materials called "spongel".

In small eardrum holes, only myringoplasty to close the hole is sufficient; membrane surgery (tympanoplasty) in which ossiculoplasty is performed for problems with middle ear ossicles in large eardrum holes may be required.
Why closure of the eardrum hole surgery performed?
Eardrum surgeries are performed in patients with permanent holes in the eardrum for the following reasons:- Restoring the eardrum barrier function. In this way, the risk of middle ear infection is eliminated if water escapes into the external ear canal.
- Improve hearing. By resurfacing the vibrating surface area of the eardrum, the vibration energy generated by the sound waves is transmitted more easily.
- Preventing the emergence of diseases and conditions such as facial palsy, brain abscess, meningitis due to prospective recurrent middle ear infections
Endoscopic Repair of Tympanic Membrane
With the endoscopic technique, it is possible to repair the hole in the eardrum through the ear canal without any external incision. Endoscopic eardrum surgeries can be performed under local or general anesthesia. After removing the dead cells located at the edges of the eardrum, overlay (underlay technique) or underlay (underlay technique) muscle membrane (fascia), cartilage membrane (perichondrium) or cartilage grafts are placed. During eardrum surgeries, fibrotic tissues and granulation tissues in the middle ear can also be removed after the membrane is removed.During the operation, especially the new membrane, the prepared graft should be contacted to all edges of the hole. In particular, the edges of the front of the hole, if the graft does not come into contact with the opening of these areas and may cause surgery to fail.
Endoscopic Eardrum Surgery Video
Endoscopically assisted eardrum surgery (Endoscopic Myringoplasty - Endoscope Assisted Myringoplasty, Endoscopic Myringoplasty - Endoscopic-Assisted Myringoplasty - Endoscopic Eardrum Hole Surgery - Endoscopic Repair of Tympanic Membrane Perforation) is shown to the patient with central hole (tympanic membrane central perforation) in the eardrum.
• aspiration of the antiseptic solution poured into the external auditory canal and local anesthetic injection
• cleaning the dead cells on the edge of the hole in the eardrum
• cleansing of the middle ear adhesions
• that blood is coming from all sides of the dice and that the receipt of dead cells is controlled
• placement of cartilage parts in the middle ear
• a cartilage graft is laid over your hole (on the eardrum membrane)
• checking that the pre-peeled dried cartilage membrane is outermost and that all hole edges are closed
• It appears that the graft that has been placed has been soaked with antibiotics and spontaneously dissolvable materials called "spongel".
Perforated Eardrum Repairing Surgery (Endoscopic Transcanal Myringoplasty) Video
Video Description: In the video above, a transcanal endoscopic myringoplasty operation was planned for the patient with a previous perforation of the eardrum, in order to treat the hole in the eardrum. After local anesthetic injection, cartilage was removed from the tragus cartilage as a graft. Island graft was prepared, perforation edges were dedepithelized. Island flap was placed as an overlay. Adrenaline-infused cottons were laid on the graft and aspirated. Perichondrium was laid on the outermost part. Sponges impregnated with antibiotics and divided into small pieces were laid on the external ear canal and grafts. Bleeding was checked. Ear pads were placed in the external ear canal and the operation was terminated.
The tympanic membrane, commonly known as the eardrum, is a critical component of the human ear. It separates the external ear from the middle ear and plays a vital role in the transmission of sound waves. When the tympanic membrane becomes damaged or perforated, it can result in hearing loss, pain, and an increased risk of ear infections. To address these issues, medical professionals often turn to endoscopic repair, a minimally invasive surgical procedure. In this article, we will explore the endoscopic repair of the tympanic membrane, including its benefits, the surgical procedure, and the recovery process.
Understanding the Tympanic Membrane
The tympanic membrane is a thin, semitransparent membrane that stretches across the ear canal, separating the outer ear from the middle ear. It is an integral part of the auditory system, as it vibrates in response to sound waves, transmitting them to the three small bones of the middle ear, known as the ossicles. These vibrations are then sent to the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical signals and processed by the brain as sound.
The tympanic membrane is remarkably sensitive and efficient, capable of detecting sound waves even at extremely low levels. However, due to its delicate nature and its location at the boundary between the external and middle ear, it is vulnerable to damage and perforations.
Causes of Tympanic Membrane Perforations
Tympanic membrane perforations, also known as eardrum perforations, can occur for various reasons. Some of the common causes include:
Infections: Severe ear infections, such as acute otitis media or chronic otitis media, can lead to the accumulation of fluid and pressure, resulting in eardrum perforation.
Trauma: Physical injury to the ear, like a direct blow or a sudden change in air pressure, can cause the eardrum to rupture.
Barotrauma: Rapid changes in air pressure, such as those experienced during scuba diving, air travel, or explosion exposure, can damage the eardrum.
Foreign objects: Inserting foreign objects into the ear canal, like cotton swabs or hairpins, can accidentally puncture the eardrum.
Acoustic trauma: Exposure to extremely loud noises or explosions can lead to eardrum damage.
The Endoscopic Repair Procedure
Endoscopic repair of the tympanic membrane is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows the surgeon to visualize and repair the eardrum with the help of an endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera attached. Here's a step-by-step overview of the procedure:
Anesthesia: The procedure is typically performed under local or general anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort and relaxation.
Access: The surgeon inserts the endoscope into the ear canal, providing a magnified view of the eardrum on a screen.
Assessment: The surgeon carefully examines the tympanic membrane and any associated structures to determine the location and extent of the perforation.
Repair: Using specialized microsurgical instruments, the surgeon can precisely repair the eardrum. The approach may involve patching the perforation with a graft, such as the patient's tissue or a synthetic material. In some cases, the ossicles may need to be adjusted or repaired as well.
Check for air-tightness: Ensuring that the repaired eardrum is air-tight is crucial for optimal hearing function. The surgeon confirms this by conducting an inflation test to see if the eardrum moves appropriately when air pressure changes.
Wound closure: Once the perforation is successfully repaired, the surgeon removes the endoscope, and the procedure is complete.
Benefits of Endoscopic Tympanic Membrane Repair
Endoscopic repair of the tympanic membrane offers several advantages over traditional open surgical techniques:
Minimally Invasive: The procedure is less invasive, resulting in smaller incisions, less scarring, and reduced discomfort.
Precise Visualization: The endoscope provides a magnified, high-definition view of the eardrum, allowing for precise repairs.
Shorter Recovery: Patients often experience a faster recovery and less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgery.
Preservation of Ear Structure: This technique is less likely to cause changes in ear canal shape or structure.
Outpatient Procedure: In some cases, endoscopic repair can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Recovery After Endoscopic Tympanic Membrane Repair
Recovery after endoscopic tympanic membrane repair varies from person to person, but there are some general guidelines to keep in mind:
Pain and Discomfort: Some mild pain or discomfort may be experienced after the surgery, but this is typically manageable with prescribed or over-the-counter pain medications.
Hearing: Hearing improvement may not be immediate, and there may be some temporary changes in hearing as the ear heals.
Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing and remove any packing material if used.
Activity Restrictions: Patients are often advised to avoid water activities and swimming for a specified period, as water exposure can increase the risk of infection.
Full Recovery: The eardrum may take several weeks to months to fully heal, and hearing may continue to improve during this time.
Endoscopic repair of the tympanic membrane is a remarkable advancement in ear surgery, offering patients a minimally invasive, effective, and precise option for addressing eardrum perforations. By leveraging advanced endoscopic technology, surgeons can provide the necessary repairs with reduced discomfort and faster recovery times. If you are facing issues with your eardrum, consult with an ear, nose, and throat specialist to determine if endoscopic tympanic membrane repair is the right solution for you.
On this website, the link group where you can read the articles I have previously published about Endoscopic Eardrum Repair >> https://www.ent-istanbul.com/search?q=Endoscopic+Eardrum+Repairy
Source links >> Endoscopic Myringoplasty and Type I Tympanoplasty - ScienceDirect / Totally endoscopic tympanic membrane repair - PubMed (nih.gov)
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47













Comments
Post a Comment