Soft Tissue Polly Beak Deformity
 Pollybeak or “parrot beak” deformity is a complication of rhinoplasty, which is described by the typical appearance of a dorsal nasal convexity that resembles a parakeet's beak. This dorsal hump is located in the supratip aea of the nose, and then causes a deformity that resembles the appearance of a beak ridge at the tip of the nose and downward rotation at the tip. The beak nose deformity defines postoperative deformity associated with supratip occupancy, which leads to a disproportionate association between tip and supratip. It can come up with various mechanisms.
Pollybeak or “parrot beak” deformity is a complication of rhinoplasty, which is described by the typical appearance of a dorsal nasal convexity that resembles a parakeet's beak. This dorsal hump is located in the supratip aea of the nose, and then causes a deformity that resembles the appearance of a beak ridge at the tip of the nose and downward rotation at the tip. The beak nose deformity defines postoperative deformity associated with supratip occupancy, which leads to a disproportionate association between tip and supratip. It can come up with various mechanisms.The beak can be a result of the technique used in nasal surgery, but it can also occur as an unpredictable complication even for the most experienced surgeons. The causes of the beak nasal deformity can be listed as the inadequate resection of the supratip structures (insufficient gut cartilage removal), overfilling of the nasal bone, loss of nasal dextrose, or abnormal edema in patients with thick suprathecal skin. An excessive cartilage resection (usually associated with thick nasal skin), which results in subcutaneous scar tissue formation in the suprathep region, is one of the most common causes. Supratip cartilage and excessive cartilage removal due to inadequate cartilage removal, when the nose of the beak emerges roughly cartilaginous beak nose deformity (cartilaginous beak nose deformity / cartilaginous pollybeak deformity) is called.
In the treatment of cartilaginous pollybeak deformities, bast cartilage tissue resections are usually sufficient for treatment. At the same time, cartilage graft placement and nasal lift can be performed to support the tip of the nose in patients with loss of nose support. The appearance of post-operative abnormal soft tissue excess due to soft tissue features and thick skin structure in the nose and supratip area may result in nasal symptoms. Beak nose deformities that appear in this way are called soft tissue beak nose deformities (soft-tissue polly beak). Treatment is more difficult in such cases. There are also tried medical treatments that can be long lasting and insufficient, such as injection of coryza under the skin, products that can reduce the skin thickness on the skin.
Pollybeak Deformity is classified in two main subgroups as I have seen above. Each subgroup emerges as a result of one or more of the following conditions:
Cartilaginous pollybeak deformities
• Excessive resection of nasal bones• Inability to cartilage dorsum
• Excessive resection of the lower lateral cartilages (leads to loss of tip support)
Soft tissue pollybeak deformities (excessive supratip fullness, supratip deformity)
• Bandage of the upper part of supratip area with overprinted bandage• Excessive skin thickening at the tip of the nose after reduction after rhinoplasty
• Insufficient correction in vestibular mucosa
• Thick soft tissue on supratip region
Especially in patients with thick skin, making the supratip break point more visible and excessive supratip reduction may prevent the emergence of Soft Tissue Pollybeak Deformity in the long term. When the surgery is completed with the supratip area and the nasal tip at the same level, soft tissue pollybeak deformity may occur as a result of the fibroadipose tissue in the supratip area being regenerated during the healing process. Before rhinoplasty, evaluation of the patient's skin characteristics and technical planning are very important. Despite all this, in some patients, fibroadipose tissue production and tissue swelling may be greater than expected and this deformity may occur.
Indeed, the characteristics of the nose skin can seriously affect the surgical success and result. It was reported in a recently published scientific study that the skin thickness over the nosebelt and nose arch could be assessed by gently squeezing between the index finger and the thumb during the examination. In fact, it was emphasized that a close examination of the tip of the nose showed that the presence of excess oil pockets (comedones) was excessive in skin thickness. So this means that after the surgery, normally more than nosebleeds, besides being the duration of edema; a rounded appearance rather than a slightly curved or angled image at the tip of the nose (thick nose skin, more camouflage ...).
Above and below, there is an abnormal difference between the skin on the nose arch supratip and the skin thickness on the nose when the skin thickness between the sign and the thumb is evaluated in the patient who developed soft tissue beak nasal deformity after the nasal aesthetic surgery. The area between the nose and the nose arch, the soft tissue, and the thick skin of the skin caused the nose to appear roughly like a beak nose.
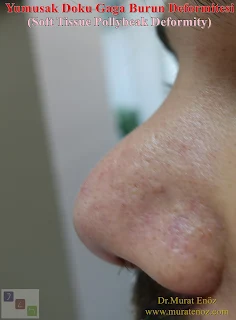 During the examination, only finger pressing on the supratip area causes the image of the beak to fall from the side. In general, steroid injections are planned as the most common medical treatment in beak nose deformities resulting from this excess soft tissue or thickening. Triamcinolone acetonide can be injected at 10 mg / mL (0.1-0.5 mL). Dermis and epidermis injections should be avoided (hypopigmentation may cause atrophy). Injection should not be administered more frequently, every 3-4 weeks. Excessive treatment may cause atrophy, which can lead to saddle nose deformities or irregular skin changes (source link >> Polly Beak Deformity in Rhinoplasty: Background, Problem ...). An application I do not like about cortisone. Although the thickening result in the supratip region is usually cortisone in a region that is far away from the eye, Steroid injections of adjoining areas (intranasal and eyelids) have been reported in the literature of post-blindness (Source: Blindness as a Complication of Subcutaneous Nasal Steroid Injection). Intralesional triamcinolone injection is the first-line treatment of soft tissue polylysomal deformities caused by subdermal scarring. If intralonezic steroid injection does Correction of the soft tissue pollybeak using triamcinolone injection). Injection depth should be subcutaneous tissue. If whitening is observed, the injection level should be considered superficial and the needle should be guided deeper. Dermic injection of triamcinolone may result in cutaneous atrophy. As is the standard practice in intralesional injection techniques, the surgeon must begin aspiration with a syringe to ensure that the needle tip is not in a blood vessel. It should not be forgotten that injecting triamcinolone into a blood drop can have dangerous consequences for the patient (source >>Correction of the Soft Tissue Pollybeak Using Triamcinolone Injection ...).
During the examination, only finger pressing on the supratip area causes the image of the beak to fall from the side. In general, steroid injections are planned as the most common medical treatment in beak nose deformities resulting from this excess soft tissue or thickening. Triamcinolone acetonide can be injected at 10 mg / mL (0.1-0.5 mL). Dermis and epidermis injections should be avoided (hypopigmentation may cause atrophy). Injection should not be administered more frequently, every 3-4 weeks. Excessive treatment may cause atrophy, which can lead to saddle nose deformities or irregular skin changes (source link >> Polly Beak Deformity in Rhinoplasty: Background, Problem ...). An application I do not like about cortisone. Although the thickening result in the supratip region is usually cortisone in a region that is far away from the eye, Steroid injections of adjoining areas (intranasal and eyelids) have been reported in the literature of post-blindness (Source: Blindness as a Complication of Subcutaneous Nasal Steroid Injection). Intralesional triamcinolone injection is the first-line treatment of soft tissue polylysomal deformities caused by subdermal scarring. If intralonezic steroid injection does Correction of the soft tissue pollybeak using triamcinolone injection). Injection depth should be subcutaneous tissue. If whitening is observed, the injection level should be considered superficial and the needle should be guided deeper. Dermic injection of triamcinolone may result in cutaneous atrophy. As is the standard practice in intralesional injection techniques, the surgeon must begin aspiration with a syringe to ensure that the needle tip is not in a blood vessel. It should not be forgotten that injecting triamcinolone into a blood drop can have dangerous consequences for the patient (source >>Correction of the Soft Tissue Pollybeak Using Triamcinolone Injection ...).
 The main treatment risk with triamcinolone injections is subcutaneous atrophy. The precise mechanism by which steroids reduce scarring is not fully understood. Corticosteroids reduce fibroblast proliferation and inflammatory responses. This effect results in reduced collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis with reduced tissue fibrosis. Corticosteroids also inhibit collagenase inhibitors and result in increased collagen degradation. Profiling and early treatments should have a greater clinical effect because they are associated with both scar proliferation and impairment.
The main treatment risk with triamcinolone injections is subcutaneous atrophy. The precise mechanism by which steroids reduce scarring is not fully understood. Corticosteroids reduce fibroblast proliferation and inflammatory responses. This effect results in reduced collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis with reduced tissue fibrosis. Corticosteroids also inhibit collagenase inhibitors and result in increased collagen degradation. Profiling and early treatments should have a greater clinical effect because they are associated with both scar proliferation and impairment.
Generally, in soft tissue beak nose treatment, it is preferable to avoid surgery if possible. Resection of scar tissue and subdermal dissection in revision surgery may cause difficulties and complications. Irregular thinning, adhesions, telengiectasia, vertical pits, grooves and possible skin loss may occur under the skin and skin. In general, subcutaneous injection of triamcinolone for scar tissue is the preferred first-line treatment for soft-tissue beak nasal deformity. If triamcinolone injections are not effective, surgical revision remains a possibility for correcting the deformity.
Indeed, the characteristics of the nose skin can seriously affect the surgical success and result. It was reported in a recently published scientific study that the skin thickness over the nosebelt and nose arch could be assessed by gently squeezing between the index finger and the thumb during the examination. In fact, it was emphasized that a close examination of the tip of the nose showed that the presence of excess oil pockets (comedones) was excessive in skin thickness. So this means that after the surgery, normally more than nosebleeds, besides being the duration of edema; a rounded appearance rather than a slightly curved or angled image at the tip of the nose (thick nose skin, more camouflage ...).
Above and below, there is an abnormal difference between the skin on the nose arch supratip and the skin thickness on the nose when the skin thickness between the sign and the thumb is evaluated in the patient who developed soft tissue beak nasal deformity after the nasal aesthetic surgery. The area between the nose and the nose arch, the soft tissue, and the thick skin of the skin caused the nose to appear roughly like a beak nose.
 During the examination, only finger pressing on the supratip area causes the image of the beak to fall from the side. In general, steroid injections are planned as the most common medical treatment in beak nose deformities resulting from this excess soft tissue or thickening. Triamcinolone acetonide can be injected at 10 mg / mL (0.1-0.5 mL). Dermis and epidermis injections should be avoided (hypopigmentation may cause atrophy). Injection should not be administered more frequently, every 3-4 weeks. Excessive treatment may cause atrophy, which can lead to saddle nose deformities or irregular skin changes (source link >> Polly Beak Deformity in Rhinoplasty: Background, Problem ...). An application I do not like about cortisone. Although the thickening result in the supratip region is usually cortisone in a region that is far away from the eye, Steroid injections of adjoining areas (intranasal and eyelids) have been reported in the literature of post-blindness (Source: Blindness as a Complication of Subcutaneous Nasal Steroid Injection). Intralesional triamcinolone injection is the first-line treatment of soft tissue polylysomal deformities caused by subdermal scarring. If intralonezic steroid injection does Correction of the soft tissue pollybeak using triamcinolone injection). Injection depth should be subcutaneous tissue. If whitening is observed, the injection level should be considered superficial and the needle should be guided deeper. Dermic injection of triamcinolone may result in cutaneous atrophy. As is the standard practice in intralesional injection techniques, the surgeon must begin aspiration with a syringe to ensure that the needle tip is not in a blood vessel. It should not be forgotten that injecting triamcinolone into a blood drop can have dangerous consequences for the patient (source >>Correction of the Soft Tissue Pollybeak Using Triamcinolone Injection ...).
During the examination, only finger pressing on the supratip area causes the image of the beak to fall from the side. In general, steroid injections are planned as the most common medical treatment in beak nose deformities resulting from this excess soft tissue or thickening. Triamcinolone acetonide can be injected at 10 mg / mL (0.1-0.5 mL). Dermis and epidermis injections should be avoided (hypopigmentation may cause atrophy). Injection should not be administered more frequently, every 3-4 weeks. Excessive treatment may cause atrophy, which can lead to saddle nose deformities or irregular skin changes (source link >> Polly Beak Deformity in Rhinoplasty: Background, Problem ...). An application I do not like about cortisone. Although the thickening result in the supratip region is usually cortisone in a region that is far away from the eye, Steroid injections of adjoining areas (intranasal and eyelids) have been reported in the literature of post-blindness (Source: Blindness as a Complication of Subcutaneous Nasal Steroid Injection). Intralesional triamcinolone injection is the first-line treatment of soft tissue polylysomal deformities caused by subdermal scarring. If intralonezic steroid injection does Correction of the soft tissue pollybeak using triamcinolone injection). Injection depth should be subcutaneous tissue. If whitening is observed, the injection level should be considered superficial and the needle should be guided deeper. Dermic injection of triamcinolone may result in cutaneous atrophy. As is the standard practice in intralesional injection techniques, the surgeon must begin aspiration with a syringe to ensure that the needle tip is not in a blood vessel. It should not be forgotten that injecting triamcinolone into a blood drop can have dangerous consequences for the patient (source >>Correction of the Soft Tissue Pollybeak Using Triamcinolone Injection ...). The main treatment risk with triamcinolone injections is subcutaneous atrophy. The precise mechanism by which steroids reduce scarring is not fully understood. Corticosteroids reduce fibroblast proliferation and inflammatory responses. This effect results in reduced collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis with reduced tissue fibrosis. Corticosteroids also inhibit collagenase inhibitors and result in increased collagen degradation. Profiling and early treatments should have a greater clinical effect because they are associated with both scar proliferation and impairment.
The main treatment risk with triamcinolone injections is subcutaneous atrophy. The precise mechanism by which steroids reduce scarring is not fully understood. Corticosteroids reduce fibroblast proliferation and inflammatory responses. This effect results in reduced collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis with reduced tissue fibrosis. Corticosteroids also inhibit collagenase inhibitors and result in increased collagen degradation. Profiling and early treatments should have a greater clinical effect because they are associated with both scar proliferation and impairment.Generally, in soft tissue beak nose treatment, it is preferable to avoid surgery if possible. Resection of scar tissue and subdermal dissection in revision surgery may cause difficulties and complications. Irregular thinning, adhesions, telengiectasia, vertical pits, grooves and possible skin loss may occur under the skin and skin. In general, subcutaneous injection of triamcinolone for scar tissue is the preferred first-line treatment for soft-tissue beak nasal deformity. If triamcinolone injections are not effective, surgical revision remains a possibility for correcting the deformity.
Apart from suggestions and techniques such as repeated steroid injection to the supratip area, nose taping techniques, and the use of Roaccutane before and after surgery, controversial suggestions such as salt restriction, use of bromelain and quercetin, and use of arnica gel can also be used to reduce the swelling of the supratip area and fibroadipose tissue production.
The above video show the use of a filler with crosslinked hyaluronic acid in the beak nasal deformity. These fillings with an effect duration of 1 year may be an alternative treatment option, albeit temporarily, except surgical treatment.

Nose Filler Injection Video For Pollybeak Deformity
The above video show the use of a filler with crosslinked hyaluronic acid in the beak nasal deformity. These fillings with an effect duration of 1 year may be an alternative treatment option, albeit temporarily, except surgical treatment.
Long-Term Pressed Taping and Casting Can Be Useful After Thick-Skinned Rhinoplasty!
Although this issue is controversial, it may be beneficial to stick a printed tape on the nose for a long time and to apply additional pressure with an aluminum splint after the operation. You can find detailed information on this subject at the link >> Taping After Rhinoplasty Is Effective For Swelling in Thick-Skinned Patients!
You can find detailed information about the Pollybeak Deformity >> https://www.ent-istanbul.com/search?q=Pollybeak+Deformity
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47



Comments
Post a Comment