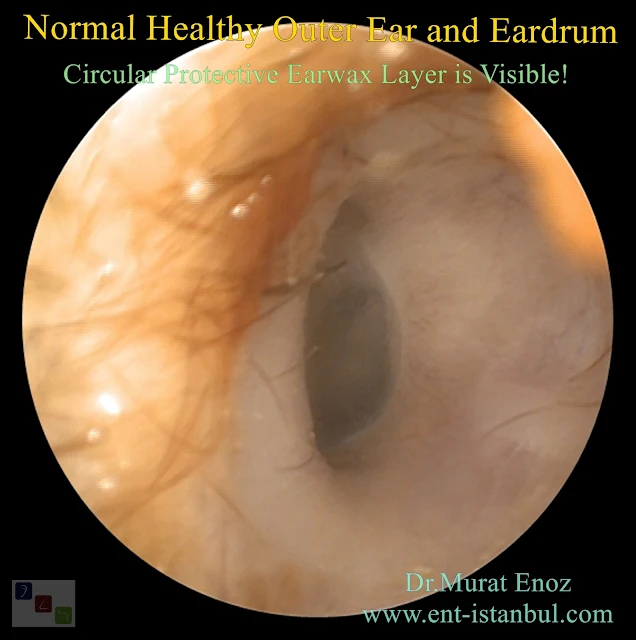
Earwax (Cerumen)
Earwax (Cerumen) is a yellowish sticky substance that is secreted into the ear canal of human and other mammals. Two types are available, the dominant wet type, and the recessive dry type earwax. Asians and Native Americans dry type earwax; In Africa and Europe, wet type (dark brown honey-brown and humid) earwax is observed.Earwax is actually a useful secretion with incredible protective properties. Benefits of earwax:
- Moisturizes the external ear canal
- Create a barrier in the outer ear and prevent the water from contacting the outer ear skin
- Antibacterial property available
- Antiviral feature available
- Prevents growth of fungi (ear mushroom - protective for otomycosis)
- There is also alcohol derivative content that prevents insects from settling in the outer ear canal
Normally the newly produced earwax is spontaneously ejected from the inside out and the external ear canal has a self-cleaning mechanism.
Chemical Composition of Earwax
Earwax is composed of a complex mixture of substances secreted primarily by sebaceous glands and ceruminous glands located in the outer ear canal. Its main components include:
Long-chain fatty acids (such as oleic acid and palmitic acid)
Cholesterol
Squalene
Triglycerides
Alcohols
Enzymes (e.g., lysozyme)
Antimicrobial peptides
Desquamated epithelial cells (dead skin cells)
This lipid-rich mixture gives earwax its viscous texture and helps it trap dust, debris, and microbes.
Antiviral Properties: Lipids and Lysozyme
Earwax's antiviral properties are primarily attributed to its lipid-based components and enzyme activity. Fatty acids such as oleic acid and palmitic acid have shown virucidal effects by disrupting the lipid membranes of certain viruses. Additionally, lysozyme, an enzyme found in cerumen, can degrade viral particles by attacking their protein coats.
Together, these components create a hostile environment for viruses, especially enveloped viruses, which are more susceptible to lipid disruption.
Antifungal Properties: Acidic pH and Unsaturated Fatty Acids
The antifungal activity of cerumen is mainly due to its acidic pH (around 4.0–5.5) and the presence of unsaturated fatty acids like oleic acid. These compounds inhibit fungal growth, particularly of Candida species and Aspergillus, which are common fungal culprits in ear infections.
The acidic environment also helps maintain a healthy ear canal microbiome, preventing fungal overgrowth.
Protection Against Insects: Sticky Texture and Squalene
Earwax provides natural protection against insects by acting as a physical and chemical repellent. Its sticky texture, derived from squalene and triglycerides, traps small invaders and deters them from entering deeper into the ear canal.
Moreover, some studies suggest that the scent produced by cerumen’s lipid degradation may serve as a chemical deterrent, discouraging insects from approaching or nesting in the ear.
Antibacterial Properties: Lysozyme, Antimicrobial Peptides, and Acidity
One of the most studied aspects of earwax is its antibacterial power. This is largely due to:
Lysozyme – an enzyme that breaks down the peptidoglycan walls of bacteria
Antimicrobial peptides – such as β-defensins and cathelicidins, which directly attack bacterial cell membranes
Acidic pH – which inhibits bacterial proliferation, especially of pathogenic strains like Staphylococcus aureus
These components work synergistically to create a protective barrier, reducing the risk of otitis externa (outer ear infections) and maintaining a healthy microbial balance.
Earwax is a prime example of how the body uses biochemical intelligence to defend itself passively. Understanding its composition and protective properties reinforces why routine earwax removal should be done with care—or not at all, unless medically necessary.
.jpg) |
| Dry Type Earwax |

 |
| Ear cotton wab - Q tip |
So why are ear cleaning cotton swabs available?
Cotton swabs should be used for cleaning the crimped and pit areas in the auricle.If you have a healthy protective layer of earwax in our ears, it's more difficult for insects to enter the outer ear canal! The substances in earwax are repulsive and irritating to many insects. If you fall asleep on grassy ground like this and have fresh, slightly viscous, oily earwax secretions in your ear, you'll feel more comfortable. Mechanically removing this layer and keeping the ear canal moist can make it easier for insects to enter, and an outer ear fungal infection (otomycosis) can also occur after contact with pool water or bathwater.
Impacted Cerumen
.bmp) |
| In the image above, you can see earwax that is close to blocking the outer ear canal. |
Especially in patients who insert cotton swabs into the outer ear canal, those with narrow ear canals, and those with hairy ears, earwax can accumulate inside the ear canal, completely blocking it and causing conductive hearing loss. In this case, patients often complain of a feeling of blockage in their ears. In such cases, it is beneficial to consult an ENT specialist. The outer ear canal can be cleaned through curettage and aspiration, and wax-softening solutions can be used to allow the earwax to pass spontaneously or make it easier to aspirate.
Search results link for articles on earwax prepared by Dr. Murat Enöz and published on this website (you can also access previous articles by clicking "more posts" at the bottom of the page) >> https://www.ent-istanbul.com/search?q=earwax
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47

.bmp)
Comments
Post a Comment