Sleep Apnea and Snoring
Sleep is a complex behavior that is vital for healthy function. Sleep is the temporary, partial and periodic discontinuation of the organism's communication with the environment in a reversible manner with various stimuli. During sleep, vital energy is stored, a large amount of growth hormone is secreted. Tissues are repaired, aging is delayed. Sedentary life, adaptation to industrial society characteristics, spending more time in the digital world and inadequate functioning of the musculoskeletal system may cause sleep apnea to occur more quickly. Especially when cardio-style exercises (such as walking with large steps, free swimming and running) are not performed, the dilator muscles of the upper respiratory tract do not work sufficiently and airway closure (collapse) becomes easier during sleep. If you cannot easily see your airway when you open your mouth and look, you need to include exercises such as walking with big steps, breathing through the nose, jogging or free swimming as a routine in your life.
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is a syndrome characterized by drowsiness in the sleep due to recurrent airway narrowing and problems caused by this condition. OSAS is characterized by recurrent respiratory arrest during sleep, decreased oxygen in the blood and increased sleepiness during the day.
Recurrent narrowing and obstruction of the upper airway in sleep can resulted with these:
* Separation of sleep
* Low sleep quality
* Daytime sleepiness
* Oxygen saturation reduction
* Cardiovascular problems
Apnea is a respiratory arrest, and this disease can be expressed briefly as a disease of respiratory arrest in sleep. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is a common syndrome seen in 2-4% of middle-aged men and in 1-2% of women. The incidence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is between 1% and 5%. Apnea is defined as cutting the air flow through the nose and mouth to the airways for 10 seconds or longer.
Hypopnea is a 50% reduction in airflow for 10 seconds and longer, along with a 3% reduction in oxygenation (oxygen saturation) of the blood. Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) is the value obtained by dividing the total number of apnea and hypopnea counts seen in sleep by the duration of sleep. Although this index is greater than 5, sleep-apnea syndrome shows a clinically significant value of 15 and above. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome is characterized by recurrent obstruction of the upper airway during sleep. This is usually accompanied by falls in the blood oxygen level. In other words, the airway is blocked at various levels. Clogging factors include swelling of the tissues surrounding the upper airway, large tonsils, large tongue, and upper respiratory tract muscles that relax in sleep. Another occlusion point may be the nose. Nasal septum deviation or turbinate hypertrophy can lead to obstruction. The jaw may be small and the structure of the upper respiratory tract may also be obstructed. There is also central apnea due to respiratory laziness without obstruction.
Risk factors for OSAS
Risk factors for sleep apnea may be listed as follows:- Obesity
- Male gender
- Age
- Neck circumference (Short and thick neck)
- Race
- Smoking, alcohol, sedative use
- Genetic factors
- Associated diseases
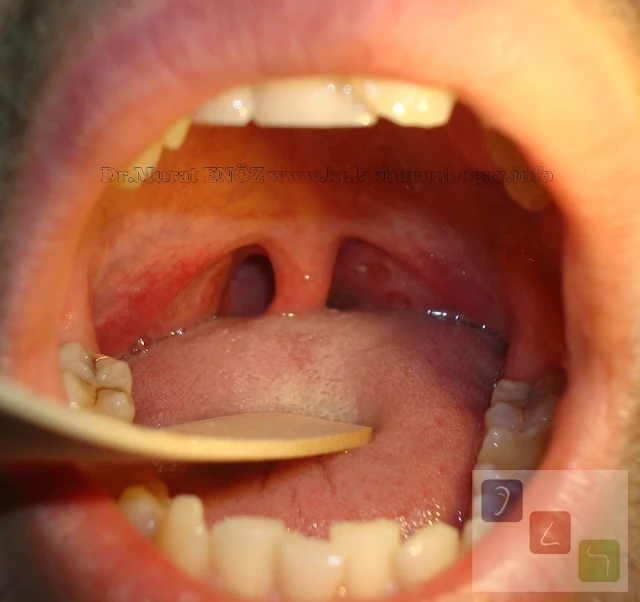
How open air hole in your throat?
When you look to open your mouth, you can see the cross-sectional area of the airway between the tonsils arrows important. Photo showing the inside of the patient's mouth with complaints such as deterioration in sleep quality, daytime tiredness, morning headaches, night sweats, back sleeping and decreased sleep satisfaction. The picture shows structurally large tonsils and a long, drooping small tongue that is prolonged.Symptoms of OSAS
Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea can be grouped as follows:Main findings
- Snore
- Witnessed apnea,
- Daytime sleepiness
Heart and Respiratory Findings
- Awakening from sleep
- Chest pain
- Night heart rhythm disorders
Nervous System findings
- Headache in the morning
- Memory issues
- Inadequate and divided sleep
- Character and personality changes
- Difficulty adapting to the environment
- Depression, anxiety
- Hyperactivity and antisocial behavior in children, failure in school
Other findings
- Dry mouth
- Night sweats
- Night Coughs
- Frequent urination at night
- Decreased sexual desire, poor performance
- Hearing loss
- Gastroesophageal reflux
Generally the OSAS patients are not aware of the situation because respiratory problems occur during sleep. The patient is immediately aware of his or her spouse or relatives. The most obvious finding is snoring. Almost all of the patients snore very violently. When the patient snores regularly, the voice is suddenly muted. The relatives of the patient first realize this. During breathing stops, abdominal and chest movements continue. Therefore, it is difficult for the air intake to stop, and the person who watches from the outside. In order to overcome the obstruction above, the diaphragm contractes more and more, and the amplitude of abdominal and chest movements increases, and after a point, when the obstruction is increased with this increased respiratory effort, the patient starts breathing again (almost like a roar), making a sound more severe than before. The first and most obvious symptom of the disease is daytime sleepiness. Other symptoms; Morning headaches waking up with severe dry mouth Morning headaches become more irritable and more intolerant than in the past Anxiety Difficulties in continuing concentration Concentration of school success in children Injury One or more times in the night without getting older The night sweats that are more pronounced than in the past and that cannot be explained by climate conditions. Impaired sexual desire in the belrigin, impotence in male patients.
Snoring
Definition of snoring: Snoring is a rough, loud sound caused by the soft palate, small tongue and the vibration of the surrounding soft tissues during sleep.In 35% of people with snoring, apnea and in 75% of cases with apnea have been reported to be snoring. Snoring rate in our country is estimated to be 10-20% and sleep apnea syndrome is estimated to be 0.9% - 1.8%. In patients with sleep apnea syndrome, snoring at least five nights or more a week occurs and irregular snoring is seen due to frequent apneas.
Snore; often occur during breathing, but may also occur during exhalation. In other words, snoring may be seen in some people with their mouth closed. Permanent snoring is seen in 44% of men between the ages of 30 and 60 and 28% of women. Snoring is an indication of increased resistance in the upper respiratory tract. In cases where resistance increases, it is seen with sleep apnea. In fact, almost all of the patients with sleep apnea have more or less snoring, while most people with snoring may not have sleep apnea. People with snoring often have narrowing in the upper airway, obesity, nasal congestion, disproportion in the face and jaw, hypothyroidism, acromegaly, tonsils and flesh growth. Snoring without sleep apnea is called ”primary snoring“ and lam simple snoring Uyku. People with snoring often do not feel uncomfortable. She often complains about this situation. The average snoring sound was found to be 60 decibels. 80-82 decibles and 90 decibels were measured in some individuals. This value is equal to the volume in rock music. Snoring is often only heard in the room where the person is sleeping, and sometimes it may be severe enough to be heard in all rooms of the house. In fact, it can cause social problems that will result in the separation of spouses' beds.
Sometimes healthy people also snore
Snoring is the noise in the form of noise occurring in cases of airway obstruction. 45% of adult people occasionally snores 25% of the time. Snoring is more common in males and obese people, but can be seen in every person. The frequency of snoring increases with age.Why do snoring occur?
The area where tongue root, small tongue, soft palate and tonsils meet with the nasal region is a self-constriction. With the relaxation of the muscles in this area during sleep, the air passage area narrows and the passing air causes vibration in the loose tissues and causes snoring. Thick and oily neck tissue in obese people, large tonsils and nasal fever in children is one of the most common causes of snoring. People with nasal obstruction create excess nasal vacuum to get air. This vacuum pulls shrinkable tissues to the airway in the throat, so that the snoring is seen when the nose is open and the snoring in the non-snoring person. Deviation problems that cause congestion, nose growth, polyps can snore. A long tongue or a small tongue of the soft palate may cause snoring by narrowing the airway. During sleep, relaxation of the tongue and throat muscles occurs. Loose muscles, especially when lying on the back of the throat behind the throat can not prevent the escape. Alcohol or sedative medication increases this muscle relaxation, and hence snoring.Why do men more snore?
This is due to the fact that lubrication is concentrated mainly in the hip region of women and in the neck and abdomen in men. Especially in overweight men, this situation increases the intra-chest pressure by lying diaphragm of the abdominal mass (especially in supine position); with the backward slipping of the tongue and sleep, the soft tissues and muscles around the pharynx are loosened and the conditions that will give rise to snoring. It is thought that differences in women's muscle structure (and perhaps estrogen hormone) also reduce snoring. After the menopause, hormonal changes in women's muscle structure begins to resemble that of men, after a certain age, their snoring rate approaching men, even equals.Witnessed apnea
Patients with sleep-apnea syndrome are usually wives or relatives who are not aware of apneas during sleep, which may cause them to consult a physician as a witness. Apnea duration is between 10-60 sec and rarely extends up to 2 minutes. This is followed by a deep and noisy breathing along with severe snoring.Extreme sleepiness during the day
Because of frequent recurrent apneas in sleep, these patients feel the need to sleep the next day. There is a parallel relationship between daytime sleepiness and the weight of sleep-apnea syndrome. Daytime sleepiness and cognitive dysfunctions increase as the number of apnea increases in the night. During the daytime sleepiness, watching television that requires little attention, while dormant while traveling; In the mid-day sleepiness, during the activities that require attention, drowsiness occurs and causes problems in the daily life of the patient. The person can sleep while driving, talking or working. Therefore, there may be problems related to traffic accidents and business life.Night heart rhythm disorders
50% of patients with sleep apnea syndrome. During apnea, first a slowing (30-50 / min) at a heart rate followed by acceleration (90-120 / min) is common.Typical chest pains usually occur due to the increased movement of the chest due to the increased breathing effort.
Waking up with a feeling of drowning in sleep and shortness of breath, 18-30% of patients with sleep-apnea syndrome occurs.
Upper airway resistance syndrome
Due to the increase in upper airway resistance, apnea is defined as recurrent sleep divisions without hypopnea and desaturation, and arousal attacks and daytime sleepiness.Is snoring a problem?
Uninterrupted, that is not accompanied by breathing disorder, snoring is called simple snoring. It was thought that the snoring did not cause any harm to the patient if he did not stop breathing and did not divide in sleep. Recent research, however, shows that simple snoring can lead to fatigue in the body, resulting in daytime fatigue and sleepiness, even if sleep-related disturbances (eg, respiratory arrest) are not present, even if the night-time breathing is relieved. Here, the noise, especially the spouse is disturbed by the environment and sleep is concerned. People who already have simple snoring, rather than the insistence of their relatives because they apply to the doctor. Snoring may be regarded as unimportant and simple by some: But sometimes it can become a problem that makes an entire household uncomfortable. It is certain that it has a negative impact on quality of life. The rest of the family is held responsible for sleepless nights. Snoring person becomes undesirable roommate on vacation and business trips. The snoring person is likely to have many medical problems. The damage to the person is greater. There are nights without rest. In people who are overly snoring, high blood pressure is more common than people who do not snore.Polysomnography
During sleep, neurological, other physiological and physical parameters of a certain period of cardiac and respiratory usually overnight, defined as the simultaneous and continuous recording. It is the most reliable diagnostic method for diagnosing sleep apnea. Sleep staging is performed in polysomnographic study; respiratory effort, breath flow, oxygen saturation, condition of the body and electrocardiography (heart radiography) and pale tone are recorded. For the diagnosis of periodic leg movements, an EMG or leg movement receiver is attached to the lower leg face.Treatment of OSAS
Successful results are obtained from snoring ans slep apnea surgeries that fix the moving tissues in the throat and further expand the airway. These operations are called uvulopalatofarengoplasti surgery (UPPP). Apart from these, different surgical combinations can be planned according to the air stenosis in the throat. In patients with nasal obstruction, treatment may be applied.. CPAP or BPAP positive pressure mouth-nose masks are used in patients whose general condition is not suitable for surgery, there is no operation due to another disease or they cannot benefit from surgery.In some mild cases, intraoral tools may be useful for some time. It is tried to reduce the snoring by providing the soft palate stiffness in the appropriate patients with the special materials called batteries placed in the soft palate. Other solution for palatal snoring treatment is "Pillar Procedure". You can find details about Pillar Palatal Implant at >> Pillar Implant System (Pillar Procedure)
General Measures
People with sleep apnea are usually overweight. Obesity is one of the most important risk factors. Patients should be directed to lose weight. It should be preferred not to lie on the back. In the back position, the tongue slides back and causes the airflow to narrow further. Therefore, the apnea of many patients increases in the supine position. The head should lie on the floor higher than the body, but avoid the high cushions that fold the neck. Factors that increase disease should be avoided; At the beginning of these factors comes alcohol and sedative drugs. It is known that alcohol increases the number and duration of apneas, and the blood decreases the oxygen rate.Medicines
Medications for patients with sleep apnea are generally unhelpful. Drugs that can correct nasal congestion can reduce snoring. Nasal expanders, for example; elastic bands can provide nose opening and reduce snoring. However, sleep apnea syndrome is not enough to treat.CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure-Continuous Positive Airway Pressure)
The CPAP contains a high-speed generator and pumping compressed air in compressed air to create an air flow at adjustable pressure.This device provides positive air pressure by means of a nose mask to keep the pale path open during the night. In sleep, breathing returns to normal and snoring stops, the oxygen level in the blood returns to normal, reducing the risk of heart disease and high blood pressure.
BPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure) Treatment of biphasic positive airway pressure
Because of BPAP (two-level positive airway pressure) obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) was applied to patients who were unable to comply with the treatment and to improve the compliance of the ventilator. BPAP devices are exhaled (exhaled) with less pressure than breathing (inspiration). This is because the tendency of airway resistance and airway closure during sleep is higher than inspiration during expiration.Intraoral devices
It has been produced with the aim of increasing the upper airway diameter by placing it into the mouth.Intraoral devices considered to be an alternative to CPAP treatment are placed in the mouth during sleep, changing the position of the upper airway structures, expanding the airway, reducing the airway resistance by acting on muscle functions and preventing the closing of the upper airway. There are two types of tools to advance the lower jaw and the tools that hold the language ahead.
Surgical treatment
Some physical problems leading to respiratory distress during sleep can be corrected by surgery. These problems; tonsils or nasal passages (mostly in children), nasal polyps, curved nose (septum deviation), impaired jaw structure, or soft palate problems.Only nasal operations are not always enough to treat sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is when the breathing stops for 10 seconds or longer during sleep. In the meantime, the level of oxygen in the blood drops, there are sleep splits. Sleep has different stages in itself. The most rested period is a period of deep sleep, and sleep apneas occur most often during this period. When the person enters the apnea from deep sleep to superficial sleep, often does not wake up fully and does not realize that the apnea. Recurrent apneas are not rested because of the deep sleep time is shortened, daytime sleepiness occurs. As the level of oxygen in the blood decreases during apnea, many vital organ apneas, including brain and heart, remain oxygen free and cause many risks including sudden death. Sleep apnea may be central (central, brain-induced) and obstructive. Central sleep apnea is much more rare and develops when the brain does not send enough signals to the diaphragm muscle and chest muscles that control breathing. Respiratory muscles are not stimulated, so there is no respiratory effort. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) occurs as a result of obstruction or contraction of the upper airways during sleep. In OSAS the person tries to breathe but can not take because the upper respiratory tract is obstructed. Although the exact cause of central sleep apnea is not known, central nervous system, nerve-muscle diseases, heart failure and chronic lung diseases are thought to have an effect. In OSAS, conditions that cause obstruction or stenosis in the upper respiratory tract are the factors. The upper respiratory tract starts from the nose and continues until the nasal area, soft palate and tongue root and larynx. Therefore, stenosis or blockages in one or more of these regions may cause OSAS. Actually, is this the cause of sleep apnea and obstruction? the result? is still being discussed. Most of the time, airway collapse area is not a single level. Nose + soft palate, soft palate + tongue root or nose + soft palate + tongue in the form of the root. Therefore, only nasal operations are not enough to treat sleep apnea.Long Time Risks and Results of Sleep-Apnea Syndrome Without Treatment
Depending on sleep apnea syndrome and long-term oxidative stress, the following risks and adverse health problems may occur:- Cardiovascular Problems
- Cerebrovascular Stroke
- Pulmonary (related to respiratory system) problems
- Psychiatric problems
- Endocrine problems (related to hormone system)
- Hematological (blood-related)problems
- Nephrologic (Urinary system) problems
- Socio-economic problems
- Sudden death
Similar links >> Children's Sleep Apnea Causes, Symptoms and Treatment / Sleep Apnea ⇒ Obesity and ⇒ Sleep Apnea Again - A Vicious Circle! / Treatment of Snoring and Sleep Apnea / How is Sleep Apnea Revealed When Lying On The Back in Deep Sleep?
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47

Comments
Post a Comment