Nasal Hyperventilation and Hypoventilation
 |
| Nasal Hyperventilation and Hypoventilation - Modified Young's Operation - Septoplasty - Turbinate Reduction With Radiofrequency |
Each tissue within our nose has different functions and functions. There are 3 structures called turbinate in each nasal cavity. They are involved in moistening, purifying, heating and pressurizing the air entering the nose. Sometimes, if these structures grow, there may be a health problem called "turbinate hypertrophy" which causes increased airway resistance in the nose. Patients may result in abnormal increase in intranasal airway resistance and nasal obstruction. In this case, applications such as radiofrequency and laser are made in order to reduce the volume of turbinate in modern techniques respecting anatomy. In addition, if these tissues are abnormally reduced or surgically removed, an abnormal airway dilation occurs within the nose, and pain may occur as a result of drying, structural changes and nerve end damage in the nasal mucosa due to contact with accelerated airflow. In patients whose turbinates are completely removed, chronic progressive mucosal damage called "Empty Nose Syndrome" and a decrease in nasal functions may occur. The patient I presented to you in the photographs is a patient who had previously undergone a turbinate radiofrequency reduction procedure and a severe decrease in the volume of the lower turbinate in the left side nasal cavity resulting in dryness, crusting and painful sores on the left side of the nose. This patient had deviation of the nasal septum and right lower turbinate hypertrophy in the right nasal cavity. Namely, nasal hyperventilation in the left nostril; hypoventilation was present in the right nostril.
At one side of nose is hyerventilation problem other side is hypoventilation problem can be seen as this case!
 |
| Septoplasty operation |
The patient whose photographs were presented here had "hypoventilation" and "increased nasal resistance" due to nasal septum deviation and turbinate hypertrophy on the right side; On the left side, there was increased airway air volume (decreased nasal resistance) and hyperventilation due to abnormally reduced inferior tubinate. The patient underwent septoplasty and radiofrequency turbinate reduction on the right side of the patient and a modified young operation on the left side.
 |
| Modified Young's Operation |
During the operation, septoplasty was performed to ensure movement of the nasal septum to the left side and to decrease the airway diameter of the left nasal cavity. Right turbinate radiofrequency reduction was performed and left Modified Young's Operation increased left nasal cavity airway resistance.
 |
| Modified Young's Operation |
Young's Operation
Young's operation definition
In the Young Procedure, it is the operation of closing the nasal cavity by forming mucocutaneous flaps and preventing the intranasal mucosa from being affected by atrophic rhinitis. This operation is roughly "closing the nostrils from the inside". According to the first definition, the nose wings are sewn in two layers from the inside: first the mucosal layer and then the skin layer. The nasal cavity is kept closed for 9 months; If the nasal crust has been removed, the nasal mucosa has become moist and functional again, these flaps are cut and the nasal cavity is ventilated again. - If the shells disappear, revision surgery is performed and the nasal airway is opened. The theory behind the procedure is to protect the closed nasal cavity from time to air contact and to restore the nasal mucosa. In addition, hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasis (HHT) disease in patients with severe nosebleeds has been used in the treatment of nosebleeds.Definition of Modified Young's Procedure
Modified Young's Operation, instead of the complete closure of the nostrils as in classical Young Surgery, partial closure of the nasal cavity; Atrophic rhinitis is a separate option used in the surgical treatment of atrophic rhinitis in the presence of various diseases where the symptoms are not very severe or the complete closure of the nasal airway cannot be tolerated (sleep apnea, lung diseases ..). It can be done using different flap techniques.How is Young Surgery Performed?
 |
| Young's Operation |

In Young Surgery, the aim is to close the nose. In the classical definition, it was defined as the removal of the skin and mucous membranes from the nose to the complete closure and suturing them in flap form. In the above photo, total incision of the nasal cavity is seen after suturing of the flaps from the vestibule region and the nasal wing removed by 3 incisions. The direction of the flaps and incision locations can be changed.
How is Modified Young Surgery Performed?
 |
| Modified Young Surgery |
Because of the partial protection of nasal breath, atrophic rhinitis symptoms are more preferred by non-severe patients.
Patient Care After Young Surgery
 |
| Modified Young Surgery |
Health problems due to excessive reduction or surgical removal of turbinates
Centuries ago, turbinates were taken as close to tons as a superfluous tissue that narrowed the airways in the nose, and then the tasks of the turbinates began to emerge more clearly as a result of nasal dryness, nosebleeds, pain and odorous crustal currents.In 1900, Holmes described the stages of surgical experience he performed with 1500 turbinectomy with the diagnosis of turbinate hypertrophy, and after the removal of turbinates, there was an increasing concern over complications such as rhinitis sicca, atrophic rhinitis, and ozena. Due to the enlarged nasal cavity resulting from turbinate resection, it was found that the nasal mucosa increased humidification capabilities and the nasal mucosa decreased, resulting in dryness, crusting and mucosal atrophy in the nasal contents (source: Turbinate Reduction Rhinoplasty: History of the Procedure, Problem ...).
Symptoms of empty nose syndrome (ENS)
 |
| Empty Nose Syndrome |
The inferior turbinates, especially the front part, are the turbinate part, which has the most role in sending air, heating, purifying and humidifying. Unfortunately, when the turbinates are completely removed, the abnormal rapid air flow in the nose unfortunately dries the mucosa within the nose, infection over time, the air intake is not suitable for the lungs, drying in the lower airways, deterioration in sleep quality in the patient, decreased exercise capacity, breathing in the nose, odor in the nose. complaints such as the emergence of discharge. In patients with Hollow Nose Syndrome, there may be permanent loss of moisture in the nasal mucosa due to abnormal intranasal airway volume and damage to nerve endings in the nose due to infection, followed by painful spots in the nose called neuropathic pain. In addition to this, from time to time in the nose, congestion sensation, crusting, scented discharge, symptoms such as smell reduction may occur. In other words, the removal or reduction of abnormal tissue in turbinate surgeries can lead to an understanding of how important and unique the tissues of turbinates are seen as a simple piece of tissue.
Respect for anatomy is very important in nose surgery!
It should be accepted that each surgical dox has specific tasks and one of them is a "nose crime" of surgical removal or over-shrinking of "turbinates". The result can be considered as "total removal of turbinates", "organ loss", and in this case full treatment has not yet been developed. Turbinate s "is unique", to produce the new human-made is not possible!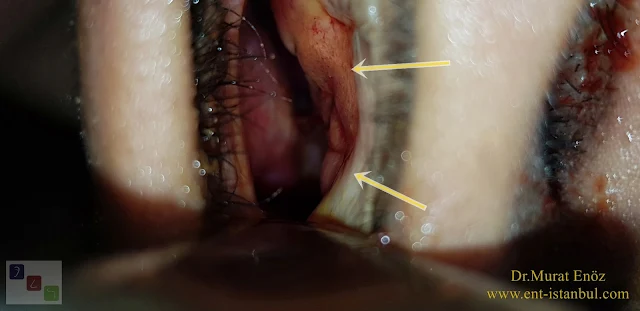 |
| Septoplasty operation |
Right Sided Modified Young Operation
Above is the intranasal view of the patient who underwent Modified Young's Operation. The patient underwent inferior turbinate total resection in a different clinic, and symptoms of empty nose syndrome appeared on the right side.
Similar links >> Why Turbinates Are Important? - Empty Nose Syndrome / Hyaluronic Acid Gel Filler Injection to Turbinates For Treatment of Empty Nose Syndrome Video / A Few Details For International Have Empty Nose Syndrome Patients Who Want to Injection of Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Filler To Turbinate / Texas Mother Suffers From Rare Empty Nose Syndrome After The Turbinate Reduction Operation
Murat Enoz, MD, Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon - ENT Doctor in Istanbul
Private Office:
Address: İncirli Cad. No:41, Kat:4 (Dilek Patisserie Building), Postal code: 34147, Bakırköy - İstanbul
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Appointment Phone: +90 212 561 00 52
Fax: +90 212 542 74 47


Comments
Post a Comment